首先肯定需要初始化一个npm项目工程啦,直接执行:
npm install -y这样不需要交互,就会直接生成一个默认的package.json:
{
"name": "sdoc-cli",
"version": "1.0.0",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"description": ""
}执行下面的命令:
npm install上面建立的是空的工程,所以其实也没有什么依赖安装,但是还是会生成一个package-lock.json文件。
我们创建index.js文件,里面打印一个hello world:
console.log(`✅ Hello, World!`);我们进入 index.js 所在目录,执行:
node ./index.js然后就会看到以下内容被打印出来:
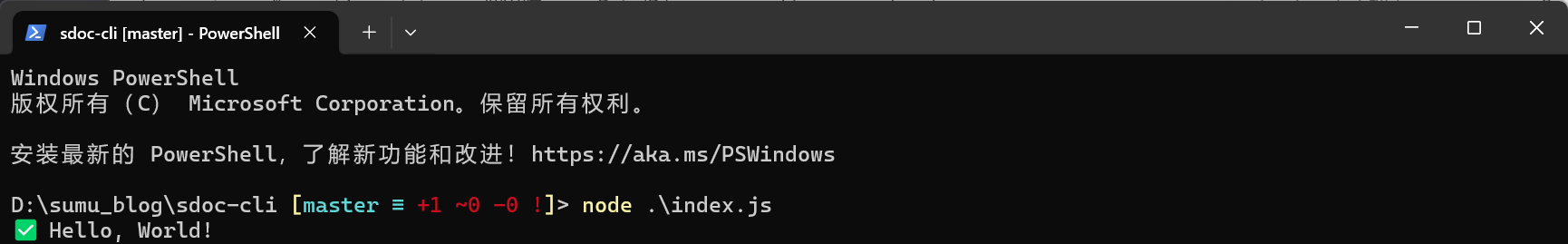
我们还可以用npm run命令,但是需要修改package.json:
{
//......
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1",
"hello": "node index.js"
},
// ......
}在script这里添加hello脚本,我们执行一下:
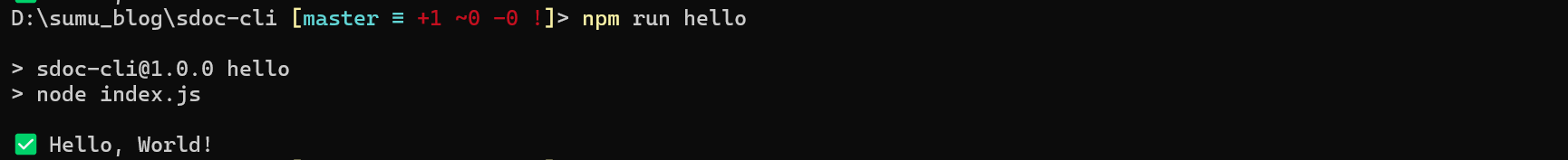
发现也是可以运行的。
上面两个只能在工程目录下运行,我要是想在命令行的任意地方运行,该怎么做?就像node、npm等命令一样。当然也可以啦。我们需要修改package.json,添加一个名为bin的键,它的值为我们自定义的命令的名称,例如:
{
//......
"bin": {
"sdoc": "./index.js"
},
//......
}然后我们就要用到npm link 命令了,它是一个非常有用的命令,用于在开发过程中将本地 npm 包链接到全局 npm 目录,从而可以在其他项目中使用这个本地包,而不需要发布到 npm 仓库。这对于本地开发和测试非常有帮助。我们进入项目的目录执行:
npm link这个命令会在全局 npm 目录中创建一个符号链接,指向我们当前的本地包,我们会看到以下打印信息:

然后会在npm全局安装目录中看到如下内容:
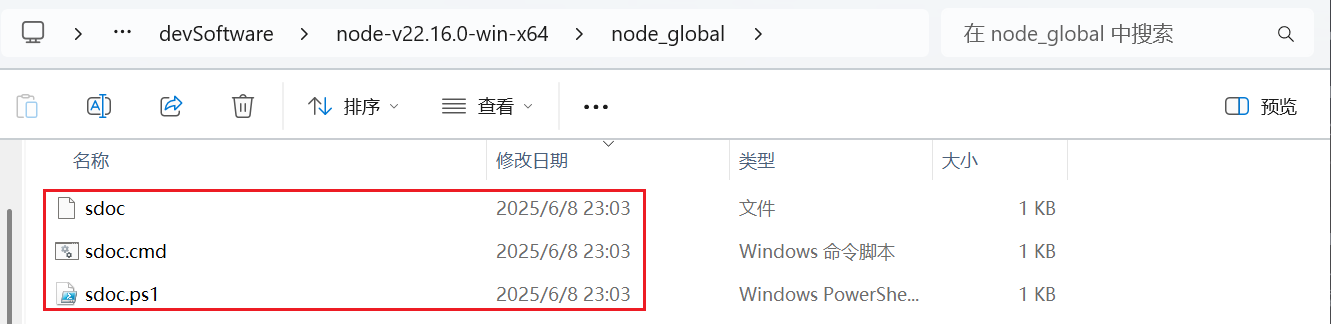
这里出现了一些文件,这些文件就算是可执行文件,也可以算是命令行的命令。我们会在全局安装目录的node_modules目录中看到这里有一个快捷方式:
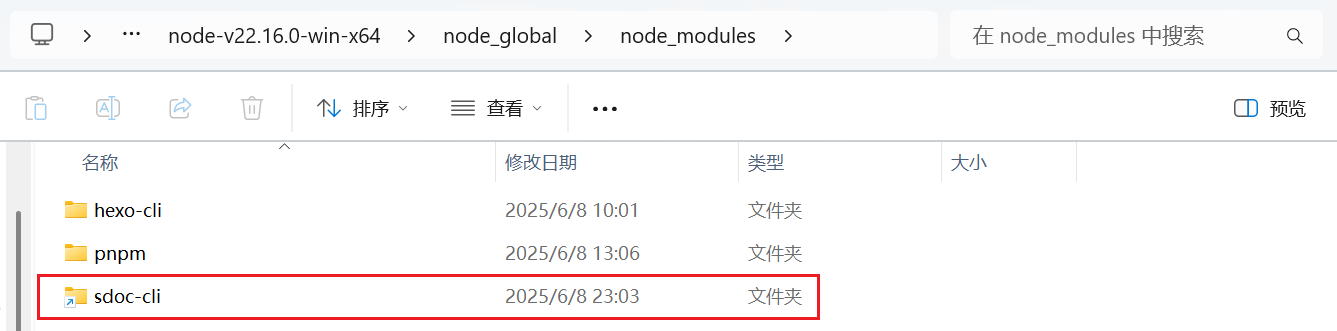
这个就是执行我们的本地npm项目了。
然后我们在命令行执行:
sdoc然后就出问题了:
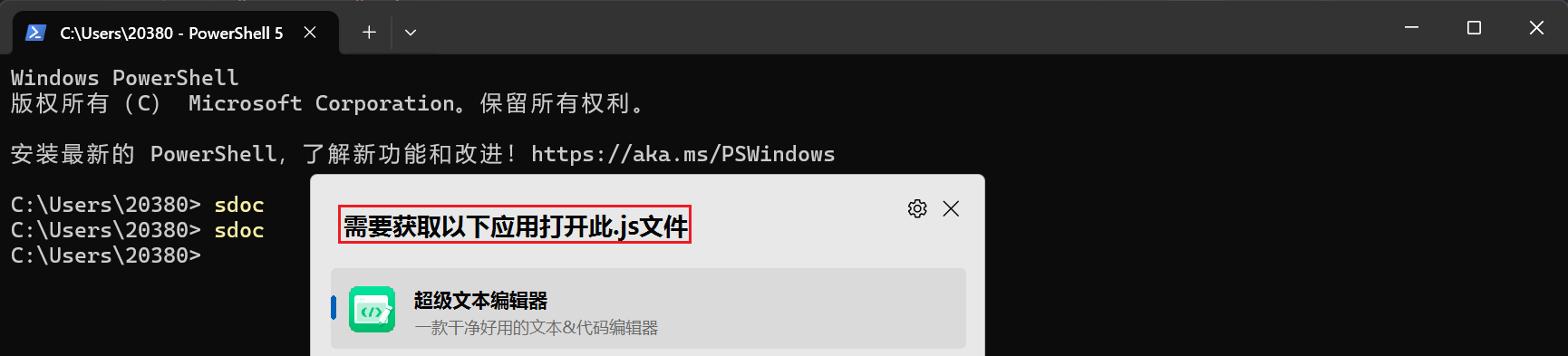
无法运行?好像是不知道要以什么应用来运行这个命令,原来是还需要修改index.js:
#!/usr/bin/env node
console.log(`✅ Hello, World!`);第一行的作用就是让系统知道这是 Node 脚本。然后重新执行npm link,再重新执行:
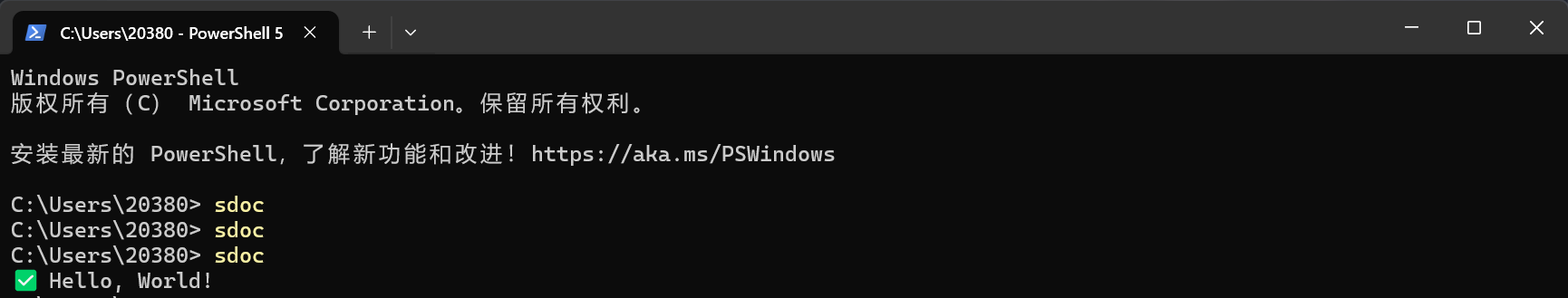
终于可以了!!!
进入sdoc-cli目录,执行:
npm un -g # 若是在其他目录,还要加上包名
npm unlink -g # 这个也可以我们在命令行执行:
npm login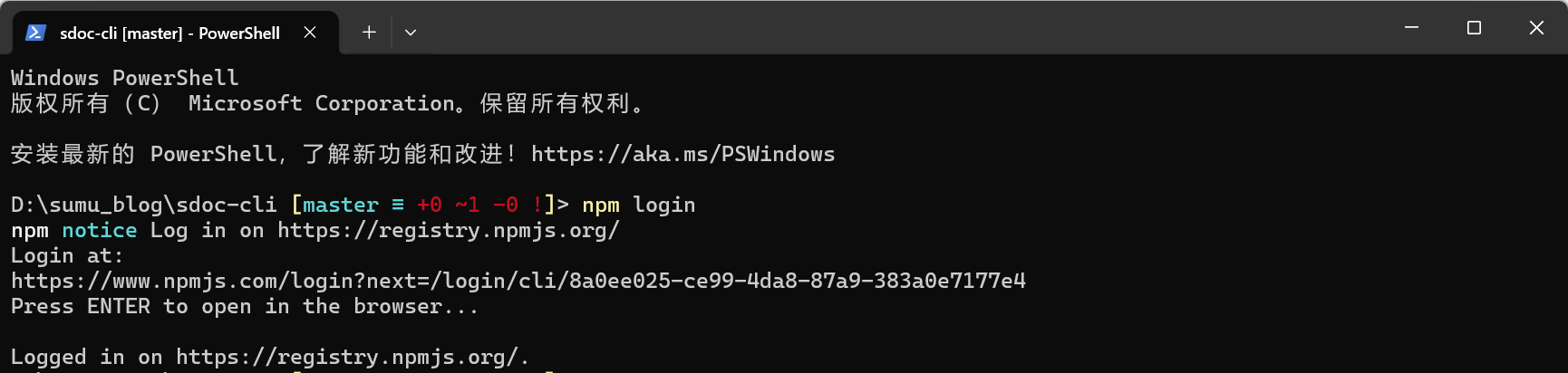
然后就会跳转到npm登录页面,登录自己的账号即可。可以通过下面的命令验证登录状态:
npm whomi
直接执行:
npm publish会看到以下输出:
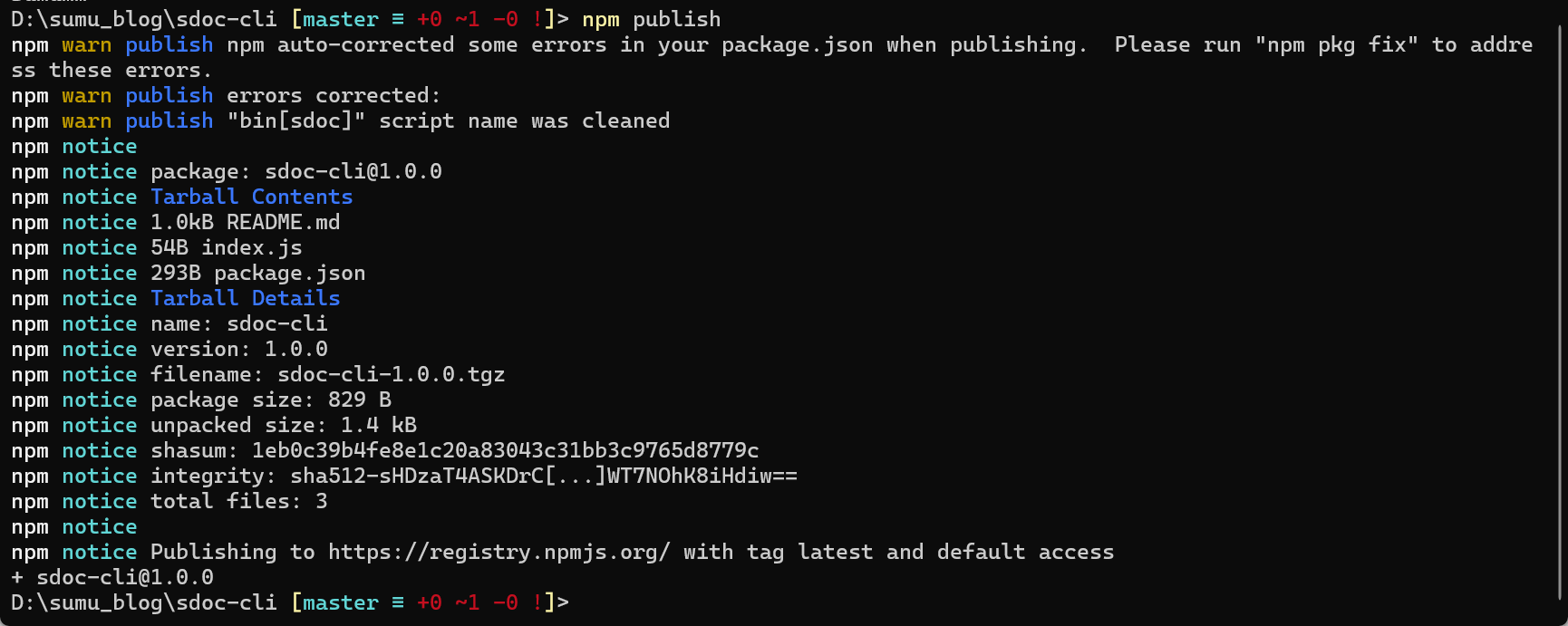
然后我们去npm个人页面看一下:
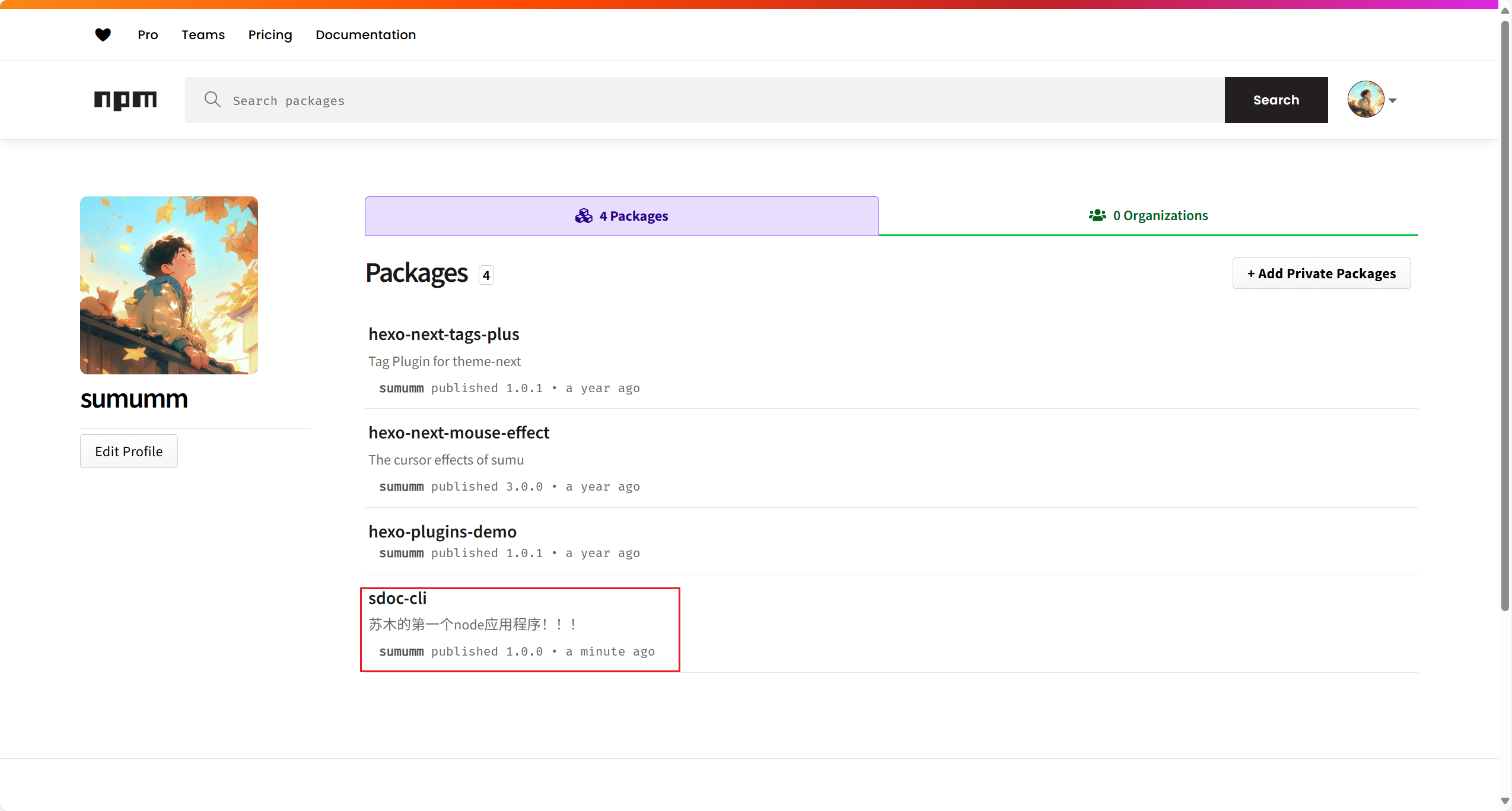
就会看到自己发布的npm包啦。
是不是可以接收一些参数,来帮我处理一些命令?比如经常写md文档,是不是可以执行 sdco n xxx.md,这样直接创建一个指定格式的md文档?
在学习c语言或者shell的时候知道,他们有argc、argv参数,可以获取到来自命令行的参数,那么javasrcipt呢?我们可以看一下Node.js文档:process 进程 | Node.js v24 文档,这里有说明。
process.argv 返回当前进程的所有命令行参数,返回值是一个数组,前2个元素是node命令路径和被执行的文件路径,我们可以看一下文档的实例:
const { argv } = require('node:process');
// print process.argv
argv.forEach((val, index) => {
console.log(`${index}: ${val}`);
});以如下方式启动 Node.js 进程:
node process-args.js one two=three four将会有以下输出:
0: /usr/local/bin/node
1: /Users/mjr/work/node/process-args.js
2: one
3: two=three
4: four所以我们自己的参数的索引是从2开始的。所以我们可以通过这种方式来获取名命令行的参数。
对于命令行参数的解析,我们有现成的模块可以使用,那就是 Commander ,commander.js 是一个广受欢迎的 Node.js 包,它为开发者提供了一套简洁而强大的 API,用于快速创建功能完备、用户友好的命令行界面(CLI)应用程序。源码仓库是 tj/commander.js,关于具体的使用方法,可以直接看文档:
npm install commander源码中为我们提供了大量的example:commander.js/examples at master · tj/commander.js · GitHub
我们修改index.js如下:
#!/usr/bin/env node
const commander = require('commander');
const program = new commander.Command();
program
.command('n')
.description('print hello world!')
.action(() => {
console.log(`✅ Hello, World!`);
});
program.parse();我们向sdoc n命令传递一个参数:
#!/usr/bin/env node
const commander = require('commander');
const program = new commander.Command();
program
.command('n')
.argument('[fileName]', 'file name', 'demo')
.description('print hello world!')
.action((fileName) => {
console.log('✅ Hello, World! fileName:', fileName);
});
program.parse();我现在主要是有两个需求,一个是按照固定模板创建md文档,另一个是替换文档中的图片相对路径,我们接下来一步一步实现这两个功能。
Node.js 的文件系统模块(fs 模块)提供了丰富的 API,用于读取、写入、删除文件以及执行其他文件系统操作。fs 模块既支持同步方法也支持异步方法,使得开发者可以根据具体需求选择合适的方式来处理文件操作。这里可以参考中文文档:fs 文件系统 | Node.js v24 文档,也可以参考Node.js 中文网 — Node.js 简介中操作文件相关部分。
Node.js 文件系统(fs 模块)模块中的方法均有异步和同步版本,例如读取文件内容的函数有异步的 fs.readFile() 和同步的 fs.readFileSync()。异步的方法函数最后一个参数为回调函数,回调函数的第一个参数包含了错误信息(error)。建议使用异步方法,比起同步,异步方法性能更高,速度更快,而且没有阻塞。
Node.js 的 readline 模块是一个用于从可读流(如 process.stdin)逐行读取数据的接口。它提供了一种简单的方式来处理命令行输入,非常适合创建交互式命令行应用程序。可以参考:readline 逐行读取 | Node.js v24 文档
我们通过fs模块来实现文件的创建和读写,通过readline模块实现
#!/usr/bin/env node
const commander = require('commander');
const fs = require('fs');
const readline = require('readline');
const program = new commander.Command(); /* 创建命令行程序实例 */
/* 创建readline接口用于用户交互 */
const rl = readline.createInterface({
input: process.stdin,
output: process.stdout
});
/* 创建markdown文件 */
async function createMarkdownFile(fileName) {
const filePath = `${fileName}.md`;
const content = `# ${fileName}\n\n`;
// 检查文件是否已存在
if (fs.existsSync(filePath)) {
const answer = await new Promise(resolve => {
rl.question(`File ${filePath} already exists. Overwrite? (y/n) `, resolve);
});
// 用户取消操作
if (answer.toLowerCase() !== 'y') {
console.log('Operation cancelled');
rl.close();
return;
}
}
// 创建/覆盖文件
fs.writeFileSync(filePath, content, 'utf8');
console.log(`Created ${filePath}`);
rl.close();
}
/* 配置命令行参数和选项 */
program
.command('n')
.argument('[fileName]', 'file name', 'demo')
.description('create markdown file!')
.action(createMarkdownFile);
/* 解析命令行参数 */
program.parse();我们进入项目目录,执行:
node .\index.js n # 创建 demo.md
node .\index.js n js文档 # 创建 js文档.md命令执行时,会先检测文件是否存在,若是存在则会提示是否覆盖,若是不存在则会直接创建。
完整的源码可以看这里:GitHub - docs-site/sdoc-cli: 我的npm命令(随着时间推移,可能更新了,但是大概逻辑是一样的)
一般静态网页的生成器在渲染markdown文档的时候都需要一些文档信息,如:
---
title: {{ title }}
date: {{ date }}
icon: famicons:logo-markdown
index: true
tags:
categories:
---
<!-- more -->我现在希望可以自动填充文件标题和创建时间,时间信息为YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS。我们把模板命名为post.md,放在scaffolds目录下。
怎么获取时间?参考一下这里:日期 - JavaScript | MDN Web 中文网,JavaScript Date 对象以独立于平台的格式表示单个时刻。Date 对象封装一个整数,表示自 UTC(纪元)1970 年 1 月 1 日午夜开始以来的毫秒数。这个可作为单独的模块,方便调用,我们编写一个 utils/sys_time.js 来实现时间的获取:
/**
* @file 日期时间工具
* @module utils/sys_time
* @description 提供日期时间格式化和处理功能
*/
/**
* 获取当前日期时间 (YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS 格式)
* @returns {string} 格式化的日期时间字符串
*/
function getCurrentDateTime() {
const now = new Date();
// 使用 padStart(2, '0') 确保单数位数字补零(如 9 → 09)
const year = now.getFullYear();
const month = String(now.getMonth() + 1).padStart(2, '0'); // 月份从0开始需+1
const day = String(now.getDate()).padStart(2, '0');
const hours = String(now.getHours()).padStart(2, '0');
const minutes = String(now.getMinutes()).padStart(2, '0');
const seconds = String(now.getSeconds()).padStart(2, '0');
return `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hours}:${minutes}:${seconds}`; // 组合成目标格式
}
module.exports = {
getCurrentDateTime
};这样们就创建了一个获取时间的模块,最后通过 module.exports 导出了一个包含函数 getCurrentDateTime 的对象,我们可以这样使用:
const getTime = require('./utils/sys_time');
console.log(getTime.getCurrentDateTime()); // 通过对象属性调用
console.log(`⏰ 创建时间: ${getTime.getCurrentDateTime()}`);读取文件我们可以使用fs模块的readFileSync函数:
/* 读取模板文件 */
function readTemplate(templatePath) {
try {
return fs.readFileSync(templatePath, 'utf8');
} catch (err) {
console.error(`❌ 模板文件读取失败: ${templatePath}`);
console.error(err.message);
process.exit(1);
}
}这里的try表示尝试执行读取文件,下面的catch表示处理错误代码,读取的时候指定 utf8 会返回字符串,可以直接处理,但是不指定返回的应该是地址。在调用的时候我们还要用到 Node.js 的 path 路径 模块来处理路径:
const path = require('path');
// 1. 确定模板路径
const templatePath = path.join(__dirname, 'scaffolds', 'post.md');
// 2. 读取模板内容
const template = readTemplate(templatePath);
console.log(template);可以读取文件了,那么怎么把里面的 {{ title }}和 {{ date }}替换成标题和时间呢?我们这个时候要用到字符串的replace方法:
/* 替换模板内容 */
function generateContent(template, name) {
return template
.replace(/{{ title }}/g, name)
.replace(/{{ date }}/g, getTime.getCurrentDateTime());
}我们传入要处理的字符串,通过replace方法全局替换。
#!/usr/bin/env node
const commander = require('commander');
const path = require('path');
const fs = require('fs');
const readline = require('readline');
const getTime = require('./utils/sys_time');
const program = new commander.Command(); /* 创建命令行程序实例 */
/* 创建readline接口用于用户交互 */
const rl = readline.createInterface({
input: process.stdin,
output: process.stdout
});
/* 读取模板文件 */
function readTemplate(templatePath) {
try {
return fs.readFileSync(templatePath, 'utf8');
} catch (err) {
console.error(`❌ 模板文件读取失败: ${templatePath}`);
console.error(err.message);
process.exit(1);
}
}
/* 替换模板内容 */
function generateContent(template, name) {
return template
.replace(/{{ title }}/g, name)
.replace(/{{ date }}/g, getTime.getCurrentDateTime());
}
/* 创建markdown文件 */
async function createMarkdownFile(fileName) {
const filePath = `${fileName}.md`;
// 1. 确定模板路径
const templatePath = path.join(__dirname, 'scaffolds', 'post.md');
// 2. 读取模板内容
const template = readTemplate(templatePath);
// 3. 生成文件内容
const content = generateContent(template, fileName);
// 检查文件是否已存在
if (fs.existsSync(filePath)) {
const answer = await new Promise(resolve => {
rl.question(`File ${filePath} already exists. Overwrite? (y/n) `, resolve);
});
// 用户取消操作
if (answer.toLowerCase() !== 'y') {
console.log('Operation cancelled');
rl.close();
return;
}
}
// 创建/覆盖文件
fs.writeFileSync(filePath, content, 'utf8');
console.log(`Created ${filePath}`);
rl.close();
console.log(`✅ 文档已生成: ${filePath}`);
console.log(`📋 使用模板: ${path.relative(process.cwd(), templatePath)}`);
console.log(`⏰ 创建时间: ${getTime.getCurrentDateTime()}`);
}
/* 配置命令行参数和选项 */
program
.command('n')
.argument('[fileName]', 'file name', 'demo')
.description('create markdown file!')
.action(createMarkdownFile);
/* 解析命令行参数 */
program.parse();