LV001-结构化提示词与输出
实验1:结构化提示词与输出
一、实验详情
目标:实现文本分类功能,返回 Pydantic 模型实例
文件位置:student_code/lab1/main.py
需要实现:classify_text() 函数
任务要求:
- 构建结构化 Prompt,要求模型输出 JSON 格式
- 调用 Ollama API 进行文本分类
- 解析 JSON 响应并创建 TextClassification 实例
- 确保返回的 category 在预定义列表中
关键要求:
- 返回
TextClassification实例(包含 category, confidence_score, keywords) - category 必须是预定义的 5 个类别之一:'新闻', '技术', '体育', '娱乐', '财经'
- confidence_score 范围 0-1
- keywords 列表长度 1-5
实现提示:
python
# 当前状态:raise NotImplementedError("请实现 classify_text 函数")
# 你需要:
# 1. 设计包含 5 个类别的 prompt
# 2. 使用 httpx.post() 调用 Ollama API (http://localhost: 11434/api/generate)
# 3. 使用 "format": "json" 参数强制 JSON 输出
# 4. 用 json.loads() 解析响应
# 5. 用 TextClassification.model_validate() 验证并创建实例测试运行:
bash
pytest grader/test_lab1.py -v测试用例:
- ✅ 返回类型验证(20%)
- ✅ 分类类别有效性(20%)
- ✅ 置信度范围检查(15%)
- ✅ 关键词非空验证(15%)
- ✅ 技术类文本准确性(15%)
- ✅ 体育类文本准确性(15%)
- 🌟 批量测试(加分项)
二、环境准备
1. 系统要求
- Python: 3.10 或更高版本
- 操作系统: Linux / macOS / Windows
- Ollama: 本地 AI 模型服务
2. 安装 Ollama
2.1 Linux / macOS
bash
# 安装 Ollama
curl -fsSL https://ollama.ai/install.sh | sh
# 启动 Ollama 服务
ollama serve
# 下载 Qwen3-8B 模型(新开一个终端)
ollama pull qwen3:8b2.2 Windows
- 访问 Ollama 官网 下载 Windows 安装包
- 安装并启动 Ollama
- 在命令提示符中运行:
ollama pull qwen3:8b
3. 验证 Ollama 服务
bash
# 检查 Ollama 是否运行
curl http://localhost:11434/api/tags
# 应该返回包含 qwen3:8b 的模型列表4. 安装 Python 依赖
bash
# 安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txtrequirements.txt 内容如下:
markdown
pydantic>=2.0.0
pytest>=7.4.0
pytest-timeout>=2.1.0
pytest-json-report>=1.5.0
httpx>=0.25.0三、pydantic
1. pydantic 简介
Pydantic 是一个在 Python 中用于 数据验证和解析 的第三方库,它现在是 Python 使用最广泛的数据验证库。它利用声明式的方式定义数据模型和 Python 类型提示的强大功能来执行数据验证和序列化,使您的代码更可靠、更可读、更简洁且更易于调试。它还可以从模型生成 JSON 架构,提供了自动生成文档等功能,从而轻松与其他工具集成。
2. 安装 pydantic
直接使用 pip 工具进行安装:
shell
pip install pydantic3. 使用示例
3.1 pydantic_example.py
python
from pydantic import BaseModel, ValidationError, Field, field_validator
from typing import Optional
import datetime
# 定义数据模型类,继承自 BaseModel
class UserModel(BaseModel):
# 基本字段定义,包含类型注解和描述信息
id: int = Field(..., description="用户唯一标识符") # 用户 ID,必须为整数
name: str = Field(..., description="用户姓名,不能为空") # 用户名,必须为字符串
email: str = Field(..., description="用户邮箱地址") # 邮箱地址
age: Optional[int] = Field(None, description="用户年龄,范围0-150") # 年龄,可选字段,默认为 None
is_active: bool = Field(True, description="用户账户是否激活") # 是否激活,默认为 True
# 自定义验证器,确保邮箱包含@符号
@field_validator('email')
@classmethod
def validate_email(cls, v):
if '@' not in v:
raise ValueError('邮箱格式不正确')
return v
# 自定义验证器,确保年龄在合理范围内
@field_validator('age')
@classmethod
def validate_age(cls, v):
if v is not None and (v < 0 or v > 150):
raise ValueError('年龄必须在0到150之间')
return v
# 示例用法
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 正确的数据示例
print("=== 正确数据示例 ===")
try:
# 创建用户数据实例
user_data = {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三",
"email": "zhangsan@example.com",
"age": 25,
"is_active": True
}
# 使用模型验证数据
user = UserModel(**user_data)
print(f"验证通过: {user}")
print(f"用户信息: ID={user.id}, 姓名={user.name}, 邮箱={user.email}")
print(f"年龄={user.age}, 激活状态={user.is_active}")
except ValidationError as e:
print(f"数据验证失败: {e}")
# 错误的数据示例
print("\n=== 错误数据示例 ===")
try:
# 创建包含错误的数据实例
invalid_user_data = {
"id": "not_a_number", # 错误:id 应该是整数
"name": "李四",
"email": "invalid-email", # 错误:邮箱格式不正确
"age": 200, # 错误:年龄超出范围
"is_active": "not_boolean" # 错误:应该是布尔值
}
# 尝试验证错误的数据
user = UserModel(**invalid_user_data)
print(f"验证通过: {user}")
except ValidationError as e:
print(f"数据验证失败:")
# 详细打印每个验证错误
for error in e.errors():
print(f" - 字段: {error['loc'][0]}, 错误: {error['msg']}")
# 缺少必需字段的示例
print("\n=== 缺少必需字段示例 ===")
try:
# 创建缺少必需字段的数据实例
incomplete_data = {
"id": 2
# 缺少 name 和 email 字段
}
# 尝试验证不完整的数据
user = UserModel(**incomplete_data)
print(f"验证通过: {user}")
except ValidationError as e:
print(f"数据验证失败:")
for error in e.errors():
print(f" - 字段: {error['loc'][0]}, 错误: {error['msg']}")3.2 运行结果
我们直接执行下面的命令运行:
shell
python .\pydantic_example.py【例】
shell
D:\sumu_blog\python-ai> python .\pydantic_example.py
=== 正确数据示例 ===
验证通过: id=1 name='张三' email='zhangsan@example.com' age=25 is_active=True
用户信息: ID=1, 姓名=张三, 邮箱=zhangsan@example.com
年龄=25, 激活状态=True
=== 错误数据示例 ===
数据验证失败:
- 字段: id, 错误: Input should be a valid integer, unable to parse string as an integer
- 字段: email, 错误: Value error, 邮箱格式不正确
- 字段: age, 错误: Value error, 年龄必须在0到150之间
- 字段: is_active, 错误: Input should be a valid boolean, unable to interpret input
=== 缺少必需字段示例 ===
数据验证失败:
- 字段: name, 错误: Field required
- 字段: email, 错误: Field required四、Pytest
1. Pytest 简介
Pytest 是一个基于 Python 的测试框架,用于编写和执行测试代码。在当今的 REST 服务中,pytest 主要用于 API 测试,尽管我们可以使用 pytest 编写简单到复杂的测试,即我们可以编写代码来测试 API、数据库、UI 等。
Pytest 的优点如下 -
- Pytest 可以并行运行多个测试,从而减少了测试套件的执行时间。
- 如果没有明确提及,Pytest 有自己的方式来自动检测测试文件和测试函数。
- Pytest 允许我们在执行期间跳过测试的子集。
- Pytest 允许我们运行整个测试套件的一个子集。
- Pytest 是免费和开源的。
- 语法简单,很容易上手。
2. 安装 Pytest
直接使用 pip 工具进行安装:
shell
pip install pytest
pip install pytest-timeout
pip install pytest-json-report3. 使用示例
3.1 test_pydantic_example.py
python
import pytest
from pydantic import ValidationError
from pydantic_example import UserModel
def test_valid_user_data():
"""测试有效的用户数据"""
# 准备有效的用户数据
user_data = {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三",
"email": "zhangsan@example.com",
"age": 25,
"is_active": True
}
# 验证数据应该通过
user = UserModel(**user_data)
# 验证字段值是否正确
assert user.id == 1
assert user.name == "张三"
assert user.email == "zhangsan@example.com"
assert user.age == 25
assert user.is_active == True
def test_valid_user_data_with_optional_fields():
"""测试带有可选字段的有效用户数据"""
# 准备带有可选字段的用户数据
user_data = {
"id": 2,
"name": "李四",
"email": "lisi@example.com"
# age和is_active使用默认值
}
# 验证数据应该通过
user = UserModel(**user_data)
# 验证字段值是否正确
assert user.id == 2
assert user.name == "李四"
assert user.email == "lisi@example.com"
assert user.age is None # age是可选字段,默认为None
assert user.is_active == True # is_active默认为True
def test_invalid_email():
"""测试无效邮箱格式"""
# 准备包含无效邮箱的数据
user_data = {
"id": 3,
"name": "王五",
"email": "invalid-email", # 无效邮箱,缺少@符号
"age": 30
}
# 验证应该抛出ValidationError异常
with pytest.raises(ValidationError) as exc_info:
UserModel(**user_data)
# 验证错误信息包含邮箱格式错误
assert "邮箱格式不正确" in str(exc_info.value)
def test_invalid_age():
"""测试无效年龄"""
# 准备包含无效年龄的数据
user_data = {
"id": 4,
"name": "赵六",
"email": "zhaoliu@example.com",
"age": 200 # 无效年龄,超出范围
}
# 验证应该抛出ValidationError异常
with pytest.raises(ValidationError) as exc_info:
UserModel(**user_data)
# 验证错误信息包含年龄范围错误
assert "年龄必须在0到150之间" in str(exc_info.value)
def test_negative_age():
"""测试负数年龄"""
# 准备包含负数年龄的数据
user_data = {
"id": 5,
"name": "钱七",
"email": "qianqi@example.com",
"age": -5 # 无效年龄,为负数
}
# 验证应该抛出ValidationError异常
with pytest.raises(ValidationError) as exc_info:
UserModel(**user_data)
# 验证错误信息包含年龄范围错误
assert "年龄必须在0到150之间" in str(exc_info.value)
def test_missing_required_fields():
"""测试缺少必需字段"""
# 准备缺少必需字段的数据
user_data = {
"id": 6
# 缺少name和email必需字段
}
# 验证应该抛出ValidationError异常
with pytest.raises(ValidationError) as exc_info:
UserModel(**user_data)
# 验证错误信息包含字段缺失错误
assert "name" in str(exc_info.value)
assert "email" in str(exc_info.value)
def test_invalid_field_types():
"""测试字段类型错误"""
# 准备包含类型错误的数据
user_data = {
"id": "not_a_number", # id应该是整数
"name": "孙八",
"email": "sunba@example.com",
"is_active": "not_boolean" # is_active应该是布尔值
}
# 验证应该抛出ValidationError异常
with pytest.raises(ValidationError) as exc_info:
UserModel(**user_data)
# 验证错误信息包含类型错误
assert "not a valid integer" in str(exc_info.value) or "Input should be a valid integer" in str(exc_info.value)
assert "not a valid boolean" in str(exc_info.value) or "Input should be a valid boolean" in str(exc_info.value)
def test_field_descriptions():
"""测试字段描述信息"""
# 获取模型的字段信息
fields = UserModel.model_fields
# 验证每个字段都有正确的描述信息
assert fields["id"].description == "用户唯一标识符"
assert fields["name"].description == "用户姓名,不能为空"
assert fields["email"].description == "用户邮箱地址"
assert fields["age"].description == "用户年龄,范围0-150"
assert fields["is_active"].description == "用户账户是否激活"
if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main([__file__, "-v"])3.2 test_failure_demo.py
python
import pytest
from pydantic import ValidationError
from pydantic_example import UserModel
def test_wrong_assertion():
"""演示断言失败的情况"""
# 创建有效的用户数据
user_data = {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三",
"email": "zhangsan@example.com",
"age": 25,
"is_active": True
}
# 创建用户实例
user = UserModel(**user_data)
# 故意写错的断言 - 这会失败,因为id实际是1,但我们断言为2
assert user.id == 2, f"期望id为2, 但实际是{user.id}"
def test_wrong_email_validation():
"""演示邮箱验证失败的情况"""
# 准备包含无效邮箱的数据
user_data = {
"id": 2,
"name": "李四",
"email": "invalid-email", # 无效邮箱
"age": 30
}
# 验证应该抛出ValidationError异常
with pytest.raises(ValidationError) as exc_info:
user = UserModel(**user_data)
# 故意写错的异常信息检查 - 这会失败,因为实际错误信息是"邮箱格式不正确"
# 但我们检查的是"邮箱地址无效"
assert "邮箱地址无效" in str(exc_info.value), f"期望错误信息包含'邮箱地址无效',但实际是: {str(exc_info.value)}"
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 运行单个测试函数来演示失败情况
print("运行测试失败演示...")
# 演示不同类型的测试失败
test_functions = [
test_wrong_assertion,
test_wrong_email_validation
]
for test_func in test_functions:
try:
print(f"\n运行 {test_func.__name__}...")
test_func()
print(f" ✓ {test_func.__name__} 通过")
except Exception as e:
print(f" ✗ {test_func.__name__} 失败: {type(e).__name__}: {e}")3.3 运行结果
- 测试通过的示例
我们直接执行下面的命令运行:
shell
python .\test_pydantic_example.py【例】
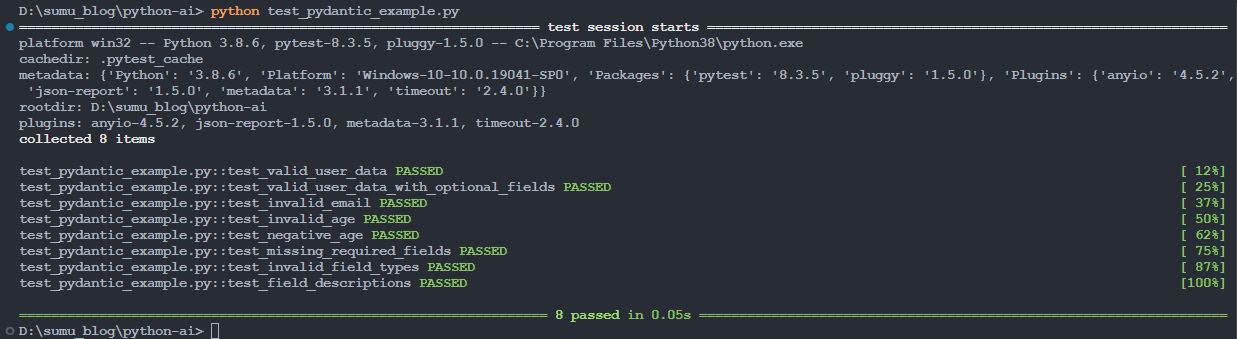
- 测试未通过的示例
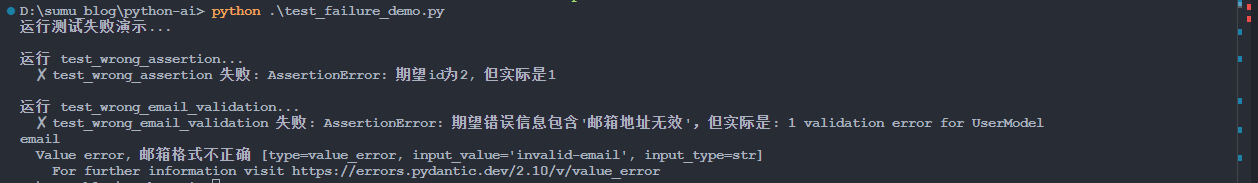
shell
python .\test_failure_demo.py【例】
五、实验示例
1. main.py
python
"""
实验1:结构化提示词与输出
学生需要实现 classify_text 函数, 使用 Pydantic 模型返回结构化的文本分类结果
"""
from typing import List
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
import httpx
import json
class TextClassification(BaseModel):
"""
文本分类结果的数据模型
"""
category: str = Field(
...,
description="文本分类类别, 必须是以下之一:'新闻', '技术', '体育', '娱乐', '财经'"
)
confidence_score: float = Field(
...,
ge=0.0,
le=1.0,
description="分类置信度, 范围0.0-1.0"
)
keywords: List[str] = Field(
...,
min_length=1,
max_length=5,
description="从文本中提取的1-5个关键词"
)
def classify_text(text: str) -> TextClassification:
"""
对输入文本进行分类, 返回结构化的分类结果
参数:
text: 待分类的文本内容
返回:
TextClassification 实例, 包含分类类别、置信度和关键词
实现要求:
1. 使用 Ollama API 调用 qwen3:8b 模型
2. 设计结构化 Prompt, 要求模型输出 JSON 格式
3. 解析模型输出并验证为 TextClassification 模型
4. category 必须是预定义的5个类别之一
5. confidence_score 必须在 0-1 范围内
6. keywords 列表长度为 1-5
提示:
- 在 Prompt 中明确指定输出格式和有效类别
- 可以使用 Few-Shot 示例提高输出稳定性
- 使用 Pydantic 的自动验证确保数据有效性
"""
# 1. 构建结构化 Prompt, 要求模型输出 JSON 格式
prompt = f"""请帮我把下面的文本进行精确的分类, 输出结果需要严格按照最后指定的格式进行输出:
要解析的文本内容为:"{text}"
文本内容分类的规则如下:
- "新闻":时事政治报道、社会热点事件、民生政策解读、国际关系动态等具有公共信息价值的报道
- "技术":人工智能发展、软件工程实践、硬件技术创新、互联网产品发布、编程开发教程等专业技术内容
- "体育":职业体育赛事、运动员竞技表现、比赛成绩播报、体育产业动态、健身健康知识等运动相关话题
- "娱乐":影视作品评析、音乐艺术创作、明星艺人动态、综艺节目内容、文化娱乐产业等休闲娱乐信息
- "财经":证券市场行情、宏观经济政策、企业财务数据、投资理财策略、金融市场监管等经济金融领域
解析要求:
1.请严格按照以下JSON格式输出, 不要包含其他文本:
{{
"category": "类别名称",
"confidence_score": "置信度",
"keywords": ["关键词1", "关键词2"]
}}
2. 根据上述规则准确分类, category必须是以下之一: '新闻', '技术', '体育', '娱乐', '财经'
2. 置信度confidence_score必须是0-1之间的小数
3. 关键词keywords要包含1-5个词, 每个词必须是字符串类型
"""
# 2. 调用 Ollama API (http://localhost:11434/api/generate)
api_url = "http://localhost:11434/api/generate"
payload = {
"model": "qwen3:0.6b",
"prompt": prompt,
"format": "json",
"stream": False
}
# 3. 解析响应中的 JSON 字符串
response = httpx.post(api_url, json=payload, timeout=30.0)
response.raise_for_status()
# 3.1 解析JSON响应
response_data = response.json()
json_str = response_data["response"]
# 3.2 解析JSON
result_dict = json.loads(json_str)
# print(result_dict)
# 4. 使用 TextClassification.model_validate() 创建实例
ret = TextClassification.model_validate(result_dict)
# 5. 返回验证后的 Pydantic 模型实例
return ret
# 测试代码(可选, 用于学生本地调试)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 测试示例
test_texts = [
"OpenAI发布GPT-5, 性能提升10倍",
"中国队在巴黎奥运会夺得金牌",
"A股市场今日大涨, 沪指突破3000点"
]
for text in test_texts:
try:
result = classify_text(text)
print(f"\n文本: {text}")
print(f"分类: {result.category}")
print(f"置信度: {result.confidence_score}")
print(f"关键词: {result.keywords}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"错误: {e}")2. 运行结果
shell
python .\main.py【例】
shell
D:\sumu_blog\python-ai\lab1> python .\main.py
文本: OpenAI发布GPT-5, 性能提升10倍
分类: 技术
置信度: 0.99
关键词: ['人工智能', '性能提升', '10倍', 'GPT-5', '发布']
文本: 中国队在巴黎奥运会夺得金牌
分类: 体育
置信度: 0.95
关键词: ['金牌', '巴黎', '奥运会', '中国队', '体育']
文本: A股市场今日大涨, 沪指突破3000点
分类: 财经
置信度: 0.95
关键词: ['股市', '上涨', '3000点', '沪市', 'A股']