LV010-记忆系统的内容检索
实验 3:记忆系统的内容检索
一、实验详情
目标:使用 LangChain 的 ConversationBufferMemory 管理会话
文件位置:student_code/lab3/main.py
需要实现:
chat_with_langchain_memory()函数:使用 LangChain Memory 进行对话get_memory_summary()函数:获取会话历史摘要
任务要求:
- 使用 LangChain 的 ConversationBufferMemory 管理历史
- 创建 LLMChain 连接 Prompt、LLM 和 Memory
- 实现 memory_variables 返回(包含 'history' 键)
- 格式化历史记录摘要为人类可读文本
关键要求:
- 使用
ConversationBufferMemory管理历史 - 返回值包含 memory_variables(含 history 键)
- 摘要格式化为人类可读文本(User: ... AI: ...)
- 不同 session 的 Memory 完全独立
实现提示:
# 需要安装和导入:
# from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
# from langchain_community.llms import Ollama
# 对于 ConversationBufferMemory 和 LLMChain:
# - 新版 LangChain 可能需要自己实现兼容层
# - 或者查找新版本的等效 API
# - 参考 LangChain 官方文档
# 提示:
# 1. 检查 session_id 是否存在对应的 Memory,不存在则创建
# 2. 创建 Ollama LLM 实例
# 3. 创建 PromptTemplate(包含历史上下文)
# 4. 创建 LLMChain,连接 Prompt、LLM 和 Memory
# 5. 运行链并获取响应
# 6. 返回响应和 memory_variablesLangChain 示例:
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(
memory_key="history",
return_messages=False
)测试运行:
pytest grader/test_lab3.py -v测试用例:
- ✅ Memory 对象类型验证(15%)
- ✅ memory_variables 结构检查(15%)
- ✅ 信息持久化验证(30%)
- ✅ 历史摘要格式(20%)
- ✅ 不存在会话处理(20%)
- 🌟 跨会话隔离(加分项)
二、环境准备
1. 系统要求
- Python: 3.10 或更高版本
- 操作系统: Linux / macOS / Windows
- Ollama: 本地 AI 模型服务
2. 安装 Ollama
2.1 Linux / macOS
# 安装 Ollama
curl -fsSL https://ollama.ai/install.sh | sh
# 启动 Ollama 服务
ollama serve
# 下载 Qwen3-8B 模型(新开一个终端)
ollama pull qwen3:8b2.2 Windows
- 访问 Ollama 官网 下载 Windows 安装包
- 安装并启动 Ollama
- 在命令提示符中运行:
ollama pull qwen3:8b
3. 验证 Ollama 服务
# 检查 Ollama 是否运行
curl http://localhost:11434/api/tags
# 应该返回包含 qwen3:8b 的模型列表4. 安装 Python 依赖
# 安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txtrequirements.txt 内容如下:
langchain==0.3.27
langchain-community>=0.0.10
pydantic>=2.0.0
pytest>=7.4.0
pytest-timeout>=2.1.0
pytest-json-report>=1.5.0
httpx>=0.25.0三、LangChain
1. 简介
LangChain 是一个用于开发由大型语言模型(LLMs)驱动的应用程序的框架。简化了 LLM 应用程序生命周期的每个阶段:
- 开发:使用 LangChain 的开源 组件 和 第三方集成 构建您的应用程序。使用 LangGraph 来构建支持一流流式传输和人工干预的有状态智能体。
- 生产化:使用 LangSmith 来检查、监控和评估您的应用程序,以便您可以持续优化并自信地部署。
- 部署:使用 LangGraph Platform 将您的 LangGraph 应用程序转化为可用于生产的 API 和助手。
LangChain 为大型语言模型及相关技术(如嵌入模型和向量存储)实现了标准接口,并集成了数百家提供商。有关更多信息,请参阅 集成 页面。
2. 架构
LangChain 框架由多个开源库组成。更多内容请参见 架构 页面。
langchain-core:聊天模型和其他组件的基础抽象。- 集成包(例如
langchain-openai、langchain-anthropic等):重要的集成已被拆分为轻量级包,由 LangChain 团队和集成开发者共同维护。 langchain:构成应用程序认知架构的链、智能体和检索策略。langchain-community:由社区维护的第三方集成。langgraph:用于将 LangChain 组件组合成具有持久性、流式传输和其他关键功能的生产就绪应用程序的编排框架。请参阅 LangGraph 文档。
3. 怎么使用?
建议:看文档 首页 - LangChain 文档
3.1 不带记忆的基本应用
3.1.1 demo.py
import sys
from langchain_community.llms import Ollama
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
# 初始化 Ollama LLM
llm = Ollama(
model="qwen3:0.6b",
base_url="http://localhost:11434"
)
# 创建提示模板
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["topic"], # 声明变量
template="请给我讲一个关于 {topic} 的简短笑话。" # 提示词模板
)
# 创建 RunnableSequence 链
chain = prompt | llm
def invoke_chain(topic, stream=False):
"""调用链并返回结果"""
if stream:
result = chain.stream({"topic": topic})
for chunk in result:
print(chunk, end="", flush=True)
else:
result = chain.invoke({"topic": topic})
print(result)
# 运行链并根据参数决定输出方式
if __name__ == "__main__":
stream_mode = "-s" in sys.argv
invoke_chain("程序员", stream=stream_mode)3.1.2 运行结果
python .\demo.py [-s] # -s 流式输出【例】

3.2 手动更新记忆的示例
3.2.1 memory_manu.py
# 导入所需的模块
from langchain_community.llms import Ollama # LangChain 的 Ollama LLM 集成
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate # 提示模板类
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory # 对话缓冲记忆类
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough # 用于传递数据的可运行对象
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser # 字符串输出解析器
# 初始化 Ollama LLM
# 使用本地部署的 qwen3:0.6b 模型,通过 11434 端口访问
llm = Ollama(
model="qwen3:0.6b", # 指定使用的模型
base_url="http://localhost:11434" # Ollama 服务的地址
)
# 创建带有记忆的提示模板
# 定义 AI 如何根据对话历史和用户输入来生成回复
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["chat_history", "human_input"], # 模板中使用的变量
template="""你是一个友好的AI助手。请根据对话历史回答用户的问题。
对话历史:
{chat_history}
用户: {human_input}
助手:""" # 提示词模板,包含对话历史和当前用户输入
)
# 初始化 ConversationBufferMemory
# 创建一个记忆对象来存储对话历史
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(
memory_key="chat_history", # 在提示模板中引用记忆的键名
human_prefix="用户", # 人类消息的前缀
ai_prefix="助手" # AI 回复的前缀
)
# 创建使用 RunnableSequence 的链
# 使用最新的 LangChain 推荐方式:prompt | llm | output_parser
def create_chain_with_memory():
"""创建带有记忆功能的链"""
def process_input(inputs):
"""处理输入,整合记忆内容"""
# 获取对话历史
chat_history = memory.buffer
# 格式化完整的提示
formatted_prompt = prompt.format(
chat_history=chat_history,
human_input=inputs["human_input"]
)
return formatted_prompt
# 创建链:输入处理 -> LLM -> 输出解析
chain = (
RunnablePassthrough.assign() # 传递原始输入数据到下一步,不做任何修改
# 确保输入字典 {"human_input": user_input} 完整传递给 process_input 函数
# 这是 LangChain 链式调用中的数据传递管道
| process_input # 格式化提示,整合记忆
| llm # 调用语言模型
| StrOutputParser() # 解析输出为字符串
)
return chain
# 创建链实例
chain = create_chain_with_memory()
def chat_with_memory(user_input):
"""
与AI进行对话,带有记忆功能
Args:
user_input (str): 用户的输入文本
"""
# 调用链进行对话,等待完整回复后一次性显示
result = chain.invoke({"human_input": user_input})
print(f"助手: {result}") # 打印完整的 AI 回复
# 手动更新记忆
memory.chat_memory.add_user_message(user_input)
memory.chat_memory.add_ai_message(result)
def show_memory():
"""显示当前的对话记忆内容"""
print("\n=== 对话历史 ===")
print(memory.buffer) # 打印存储的对话历史
print("=== 历史结束 ===\n")
def clear_memory():
"""清空对话记忆,重置对话状态"""
memory.clear() # 清空记忆缓冲区
print("对话记忆已清空")
# 主程序入口
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 默认模式:演示记忆功能的基本用法
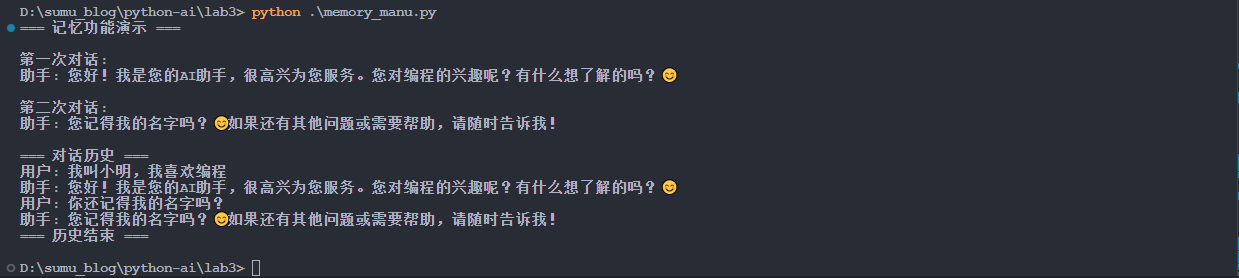
print("=== 记忆功能演示 ===")
# 第一次对话:介绍自己
print("\n第一次对话:")
chat_with_memory("我叫小明,我喜欢编程")
# 第二次对话:测试 AI 是否记住用户信息
print("\n第二次对话:")
chat_with_memory("你还记得我的名字吗?")
# 显示完整的对话记忆,验证记忆功能
show_memory()3.2.2 运行结果
python .\memory_manu.py【例】
3.3 内置记忆管理的示例
3.3.1 memory_LLMChain.py
# 导入所需的模块
from langchain_community.llms import Ollama # LangChain 的 Ollama LLM 集成
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate # 提示模板类
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory # 对话缓冲记忆类
from langchain.chains import LLMChain # LLM 链类,提供内置记忆管理
# 全局 Memory 实例
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(
memory_key="chat_history", # 在提示模板中引用记忆的键名
human_prefix="用户", # 人类消息的前缀
ai_prefix="助手", # AI 回复的前缀
return_messages=True # 返回消息对象而非字符串
)
def create_chain_with_memory() -> LLMChain:
"""
创建带有自动记忆管理的LLMChain
Returns:
LLMChain: 配置好的链实例
"""
# 初始化 Ollama LLM
llm = Ollama(
model="qwen3:0.6b", # 指定使用的模型
base_url="http://localhost:11434" # Ollama 服务的地址
)
# 创建提示模板
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["chat_history", "human_input"],
template="""你是一个友好的AI助手。请根据对话历史回答用户的问题。
对话历史:
{chat_history}
用户: {human_input}
助手:"""
)
# 创建 LLMChain,自动管理记忆
chain = LLMChain(
llm=llm,
prompt=prompt,
memory=memory # LLMChain 会自动处理记忆的保存和检索
)
return chain
def chat_with_memory(user_input: str) -> str:
"""
与AI进行对话,使用LLMChain的自动记忆管理
Args:
user_input (str): 用户的输入文本
Returns:
str: AI的回复
"""
# 创建带有记忆的链
chain = create_chain_with_memory()
# 调用链进行对话,LLMChain 会自动保存对话到记忆中
result = chain.invoke({
"human_input": user_input,
# chat_history 会由 memory 自动提供
})
# 提取 AI 回复
response = result.get("text", "") if isinstance(result, dict) else str(result)
return response
def get_memory_summary() -> str:
"""
获取完整的历史记录摘要
Returns:
str: 格式化的历史记录字符串
"""
history_messages = memory.buffer if hasattr(memory, 'buffer') else []
# 格式化消息历史为可读字符串
formatted_history = []
if history_messages:
for message in history_messages:
# 处理消息对象
if hasattr(message, 'type'):
if message.type == 'human':
formatted_history.append(f"用户: {message.content}")
elif message.type == 'ai':
formatted_history.append(f"助手: {message.content}")
elif isinstance(message, dict):
role = message.get('role', '')
content = message.get('content', '')
if role in ['user', 'human', 'User']:
formatted_history.append(f"用户: {content}")
elif role in ['assistant', 'ai', 'Assistant']:
formatted_history.append(f"助手: {content}")
else:
# 其他情况,转换为字符串
formatted_history.append(str(message))
return "\n".join(formatted_history) if formatted_history else "暂无对话记录"
def show_memory():
"""显示对话记忆内容"""
print("\n=== 对话历史 ===")
print(get_memory_summary())
print("=== 历史结束 ===\n")
def clear_memory():
"""清空对话记忆"""
memory.clear()
print("对话记忆已清空")
# 主程序入口
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 默认模式:演示记忆功能
print("=== LLMChain 自动记忆管理演示 ===")
# 第一次对话:介绍自己
print("\n第一次对话:")
print("用户: 我叫小明,我喜欢编程")
response1 = chat_with_memory("我叫小明,我喜欢编程")
print(f"助手: {response1}")
# 第二次对话:测试 AI 是否记住用户信息
print("\n第二次对话:")
print("用户: 你还记得我的名字吗?")
response2 = chat_with_memory("你还记得我的名字吗?")
print(f"助手: {response2}")
# 显示完整的对话记忆
show_memory()
# 清空记忆
print("\n清空记忆后:")
clear_memory()
# 再次对话,验证记忆已清空
print("\n清空记忆后的对话:")
print("用户: 我叫什么?")
response3 = chat_with_memory("我叫什么?")
print(f"助手: {response3}")
show_memory()3.3.2 运行结果
python .\memory_LLMChain.py【例】
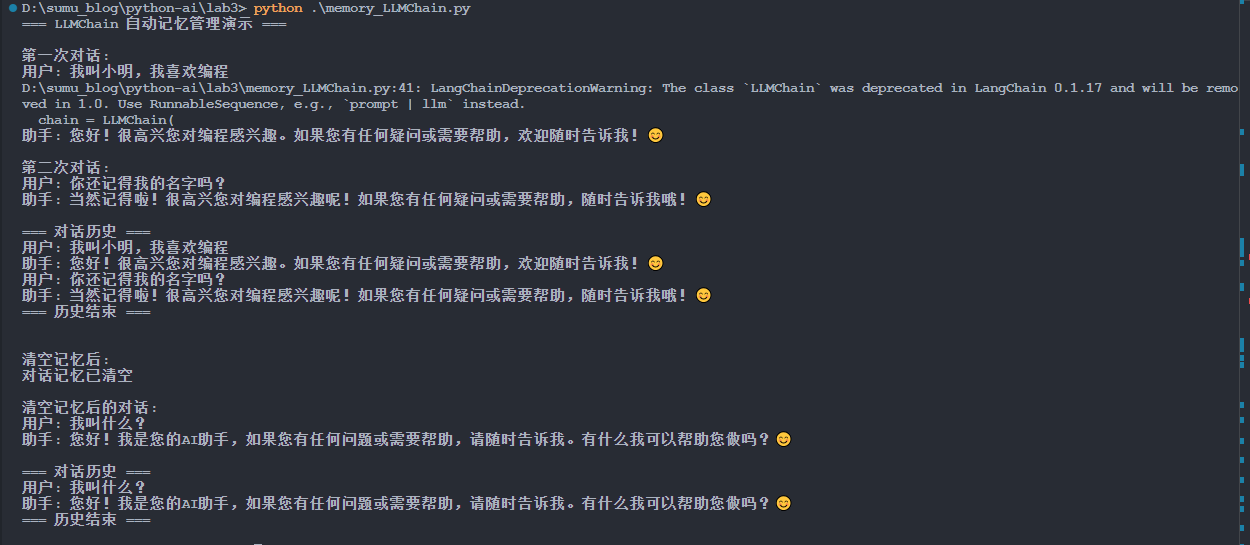
这种方式实现了自动管理记忆,但是 LLMChain 这个 api 接口在后续新版本可能会被弃用,就会出现警告。
3.4 另一种自动管理的方式
3.4.1 rwmh.py
# 导入所需的模块
import sys # 系统相关功能,用于处理命令行参数
from langchain_community.llms import Ollama # LangChain 的 Ollama LLM 集成
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, MessagesPlaceholder # 提示模板类
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory # 对话缓冲记忆类
from langchain.schema import HumanMessage, AIMessage # 消息类型定义
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableWithMessageHistory # 消息历史管理
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser # 字符串输出解析器
from langchain_core.chat_history import InMemoryChatMessageHistory # 聊天历史管理
# 初始化 Ollama LLM
llm = Ollama(
model="qwen3:0.6b", # 指定使用的模型
base_url="http://localhost:11434" # Ollama 服务的地址
)
# 创建使用 ChatPromptTemplate 的提示模板
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "你是一个友好的AI助手。请根据对话历史回答用户的问题。"),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="history"), # 消息历史占位符
("human", "{human_input}") # 用户输入
])
# 创建内存中的聊天历史存储
chat_history = InMemoryChatMessageHistory()
def create_chain_with_history():
"""
创建带有自动消息历史管理的链
Returns:
RunnableWithMessageHistory: 配置好的链实例
"""
# 基础链:提示模板 -> LLM -> 输出解析
base_chain = prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
# 包装为带有消息历史的链
chain_with_history = RunnableWithMessageHistory(
base_chain,
# 获取聊天历史的函数
lambda session_id: chat_history,
# 输入消息的键名
input_messages_key="human_input",
# 历史消息的键名
history_messages_key="history",
)
return chain_with_history
def chat_with_memory(user_input: str) -> str:
"""
与AI进行对话,使用RunnableWithMessageHistory的自动记忆管理
Args:
user_input (str): 用户的输入文本
Returns:
str: AI的回复
"""
# 创建带有消息历史的链
chain = create_chain_with_history()
# 调用带有消息历史的链进行对话
# RunnableWithMessageHistory 会自动管理对话历史
result = chain.invoke(
{"human_input": user_input},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": "default_session"}} # 会话 ID 用于区分不同的对话
)
# RunnableWithMessageHistory 会自动将对话添加到历史中
# 不需要手动更新记忆
return result
def get_memory_summary() -> str:
"""
获取完整的历史记录摘要
Returns:
str: 格式化的历史记录字符串
"""
# 获取聊天历史中的所有消息
messages = chat_history.messages
# 格式化消息历史为可读字符串
formatted_history = []
if messages:
for message in messages:
if isinstance(message, HumanMessage):
formatted_history.append(f"用户: {message.content}")
elif isinstance(message, AIMessage):
formatted_history.append(f"助手: {message.content}")
return "\n".join(formatted_history) if formatted_history else "暂无对话记录"
def show_memory():
"""显示对话记忆内容"""
print("\n=== 对话历史 ===")
print(get_memory_summary())
print("=== 历史结束 ===\n")
def clear_memory():
"""清空对话记忆"""
chat_history.clear()
print("对话记忆已清空")
# 主程序入口
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 默认模式:演示记忆功能
print("=== RunnableWithMessageHistory 自动记忆管理演示 ===")
# 第一次对话:介绍自己
print("\n第一次对话:")
print("用户: 我叫小明,我喜欢编程")
response1 = chat_with_memory("我叫小明,我喜欢编程")
print(f"助手: {response1}")
# 第二次对话:测试 AI 是否记住用户信息
print("\n第二次对话:")
print("用户: 你还记得我的名字吗?")
response2 = chat_with_memory("你还记得我的名字吗?")
print(f"助手: {response2}")
# 显示完整的对话记忆
show_memory()
# 清空记忆
print("\n清空记忆后:")
clear_memory()
# 再次对话,验证记忆已清空
print("\n清空记忆后的对话:")
print("用户: 我叫什么?")
response3 = chat_with_memory("我叫什么?")
print(f"助手: {response3}")
show_memory()3.4.2 运行结果
python .\rwmh.py【例】
D:\sumu_blog\python-ai\lab3> python .\rwmh.py
=== RunnableWithMessageHistory 自动记忆管理演示 ===
第一次对话:
用户: 我叫小明,我喜欢编程
助手: 小明,很高兴你喜欢编程!编程就像解决问题一样,能让你发现世界的奥秘呢!如果你有任何疑问或者想尝试新的编程技巧,欢迎告诉我,我们一起帮你一起进步哦!
😊
第二次对话:
用户: 你还记得我的名字吗?
助手: 当然记得啦!我是小明,很高兴和你交流!有什么问题或者想尝试新技能,随时告诉我哦!😊
=== 对话历史 ===
用户: 我叫小明,我喜欢编程
助手: 小明,很高兴你喜欢编程!编程就像解决问题一样,能让你发现世界的奥秘呢!如果你有任何疑问或者想尝试新的编程技巧,欢迎告诉我,我们一起帮你一起进步哦!
😊
用户: 你还记得我的名字吗?
助手: 当然记得啦!我是小明,很高兴和你交流!有什么问题或者想尝试新技能,随时告诉我哦!😊
=== 历史结束 ===
清空记忆后:
对话记忆已清空
清空记忆后的对话:
用户: 我叫什么?
助手: 您好!我是您的助手,请问您今天有什么问题吗?
=== 对话历史 ===
用户: 我叫什么?
助手: 您好!我是您的助手,请问您今天有什么问题吗?
=== 历史结束 ===4. 记忆管理
通过上面的三个示例,我们知道 LangChain 提供了多种对话记忆管理方式,每种方式都有其适用场景和优缺点。下面再详细分析一下这三种不同的记忆管理实现方式:
(1)手动记忆管理:需要开发者手动保存和加载对话历史
(2)LLMChain 内置记忆管理:利用 LLMChain 的内置记忆机制
(3)RunnableWithMessageHistory 自动记忆管理:使用现代化的自动记忆管理组件
| 特性 | 手动记忆管理 | LLMChain 内置记忆管理 | RunnableWithMessageHistory |
|---|---|---|---|
| 自动化程度 | 低 - 需要手动保存 | 中 - 自动保存 | 高 - 完全自动化 |
| 代码复杂度 | 高 | 中 | 低 |
| 灵活性 | 高 | 中 | 中 |
| 消息类型支持 | 自定义 | 标准格式 | 标准格式 |
| 会话管理 | 需要手动实现 | 需要手动管理 | 内置会话管理 |
| 推荐场景 | 需要精细控制 | 简单对话应用 | 现代化应用开发 |
4.1 手动记忆管理
4.1.1 实现原理
# 初始化记忆
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(
memory_key="chat_history",
human_prefix="用户",
ai_prefix="助手"
)
# 对话后手动保存
memory.chat_memory.add_user_message(user_input)
memory.chat_memory.add_ai_message(response)4.1.2 优缺点
- 优点
(1)完全控制:开发者可以精确控制何时保存、如何保存
(2)灵活性高:可以自定义保存逻辑,如过滤敏感信息、添加元数据等
(3)易于理解:记忆管理逻辑清晰可见
- 缺点
(1)代码冗余:每次对话都需要手动调用保存方法
(2)容易出错:忘记保存会导致记忆丢失
(3)维护成本高:需要手动处理各种边界情况
4.1.3 适用场景
- 需要精细控制记忆存储的应用
- 有特殊记忆处理需求的场景
- 小型项目或学习示例
4.2 LLMChain 内置记忆管理
4.2.1 实现原理
# 创建 LLMChain,自动管理记忆
chain = LLMChain(
llm=llm,
prompt=prompt,
memory=memory # LLMChain 会自动处理记忆的保存和检索
)
# 调用链时自动保存
result = chain.invoke({
"human_input": user_input,
# chat_history 会由 memory 自动提供
})4.2.2 优缺点
- 优点
(1)半自动化:LLMChain 自动保存记忆,无需手动调用
(2)集成度高:记忆管理与 LLM 调用紧密结合
(3)代码简洁:减少重复的记忆管理代码
- 缺点
(1)灵活性有限:记忆管理逻辑被封装在 LLMChain 中
(2)会话管理复杂:需要手动管理多个会话的记忆实例
(3)提示模板限制:需要按照 LLMChain 的格式设计提示模板
4.2.3 适用场景
- 简单的对话应用
- 需要快速实现记忆功能的项目
- 对代码简洁性要求较高的场景
4.3 RunnableWithMessageHistory
4.3.1 实现原理
def create_chain_with_history():
# 基础链:提示模板 -> LLM -> 输出解析
base_chain = prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
# 包装为带有消息历史的链
chain_with_history = RunnableWithMessageHistory(
base_chain,
# 获取聊天历史的函数
lambda session_id: chat_history,
# 输入消息的键名
input_messages_key="human_input",
# 历史消息的键名
history_messages_key="history",
)
return chain_with_history
# 调用时自动管理历史
chain = create_chain_with_history()
result = chain.invoke(
{"human_input": user_input},
config={"configurable": {"session_id": "default_session"}}
)4.3.2 优缺点
- 优点
(1)完全自动化:无需任何手动保存操作
(2)现代化设计:使用 LangChain 推荐的最新 API
(3)会话管理:内置会话 ID 管理,支持多会话
(4)类型安全:保持消息的原始类型和元数据
(5)代码简洁:记忆管理逻辑完全透明
- 缺点
(1)学习曲线:需要理解新的 API 设计模式
(2)配置复杂:需要正确配置各种参数
(3)依赖特定结构:提示模板需要使用特定的格式
4.3.3 适用场景
- 现代化的对话应用开发
- 需要支持多会话的应用
- 对代码质量和可维护性要求高的项目
- 企业级应用开发
4.4 核心概念解析
4.4.1 ConversationBufferMemory
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(
memory_key="chat_history", # 在提示模板中引用记忆的键名
human_prefix="用户", # 人类消息的前缀
ai_prefix="助手", # AI 回复的前缀
return_messages=True # 返回消息对象而非字符串
)作用:存储对话历史的内存缓冲区
memory_key:在提示模板中使用的变量名human_prefix和ai_prefix:格式化历史消息时的前缀return_messages:控制返回消息对象还是字符串
4.4.2 ChatPromptTemplate
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "你是一个友好的AI助手。请根据对话历史回答用户的问题。"),
MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="history"), # 消息历史占位符
("human", "{human_input}") # 用户输入
])设计理念:
- 系统消息:定义 AI 的角色和行为准则
- MessagesPlaceholder:为历史消息预留位置,支持消息类型和元数据
- 用户输入:接收当前的用户输入
为什么使用 MessagesPlaceholder 而不是字符串占位符:
(1)类型安全:保持消息的原始类型(HumanMessage、AIMessage)
(2)元数据保留:保留时间戳、角色等额外信息
(3)自动格式化:自动处理消息列表的格式化
4.4.3 RunnableWithMessageHistory
chain_with_history = RunnableWithMessageHistory(
base_chain, # 基础链
lambda session_id: chat_history, # 获取历史记录的函数
input_messages_key="human_input", # 输入消息的键名
history_messages_key="history", # 历史消息的键名
)工作机制:
(1)历史注入:自动从指定的历史存储中获取历史消息
(2)提示填充:将历史消息插入到 MessagesPlaceholder 位置
(3)链执行:执行基础链并获取结果
(4)历史更新:自动将新的消息添加到历史存储中
参数说明:
base_chain:不包含历史管理的基础链,这是主要业务逻辑,包括 LLM 调用和输出解析,例如:prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()。基础链是实际执行 AI 推理的核心。get_session_history:获取指定会话历史的函数。主要是根据会话 ID 获取对应的历史记录,session_id 是用于区分不同会话的唯一标识符。函数返回对应会话的历史存储对象。(为什么必须?RunnableWithMessageHistory 需要知道从哪里获取历史记录,以及如何存储新记录)。在我们的例子中使用 lambda 是因为只有一个全局的 chat_history,但在多会话场景中,通常会返回不同的历史对象.
# 使用字典管理多个会话的历史
session_histories = {}
def get_session_history(session_id: str) -> InMemoryChatMessageHistory:
if session_id not in session_histories:
session_histories[session_id] = InMemoryChatMessageHistory()
return session_histories[session_id]input_messages_key:输入消息在输入字典中的键名。这个键名必须与我们的提示模板中用户输入变量的名称匹配,在我们的例子中,提示模板使用{human_input},所以这里设置为"human_input"。(为什么必须?RunnableWithMessageHistory 需要知道哪个输入是当前的用户消息,以便将其与历史消息区分开)。
# 提示模板中的变量名
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("human", "{user_question}") # 这里使用 user_question
])
# RunnableWithMessageHistory 中的键名
input_messages_key="user_question" # 必须完全匹配history_messages_key:历史消息在提示模板中的键名。这个键名必须与提示模板中MessagesPlaceholder的variable_name匹配。在我们的例子中,MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="history"),所以这里设置为"history"。(为什么必须?RunnableWithMessageHistory 需要知道将历史消息插入到提示模板的哪个位置)。python# 提示模板中的占位符变量名 prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([ MessagesPlaceholder(variable_name="chat_history") # 这里使用 chat_history ]) # RunnableWithMessageHistory 中的键名 history_messages_key="chat_history" # 必须完全匹配
这四个参数协同工作,形成完整的历史管理流程:
(1)输入处理:RunnableWithMessageHistory 接收输入字典,如 {"human_input": "你好"}。
(2)历史获取:调用 get_session_history("default_session") 获取历史记录。
(3)提示构建:
- 将当前用户输入(通过
input_messages_key找到)插入到提示模板。 - 将历史消息(通过
history_messages_key找到到占位符)插入到提示模板。
(4)链执行:执行 base_chain 进行 AI 推理。
(5)历史更新:将新的用户输入和 AI 回复保存到历史记录中。
如果缺少某个参数会发生什么?
- 缺少
base_chain:没有核心处理逻辑,无法进行 AI 推理- 缺少
get_session_history:无法获取历史记录,每次对话都是全新的- 缺少
input_messages_key:不知道哪个输入是当前用户消息- 缺少
history_messages_key:不知道历史消息应该插入到提示模板的哪个位置因此,这四个参数都是
RunnableWithMessageHistory正常工作所必需的,它们共同构成了完整的自动记忆管理系统。
4.4.4 InMemoryChatMessageHistory
chat_history = InMemoryChatMessageHistory()作用:内存中的聊天历史存储。
- 线程安全:支持多线程环境
- 类型支持:支持 HumanMessage、AIMessage 等标准消息类型
- 操作简单:提供 clear()、add_message()等简单方法
四、实验示例
1. main.py
"""
实验3:记忆系统的内容检索
学生需要使用 LangChain 的 ConversationBufferMemory 管理会话历史
"""
from typing import Dict
# 提示:需要导入 LangChain 相关模块
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_community.llms import Ollama
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
# 全局 Memory 映射:{session_id: ConversationBufferMemory 实例}
SESSION_MEMORIES: Dict[str, ConversationBufferMemory] = {} # TODO: 将 any 替换为正确的类型
def chat_with_langchain_memory(message: str, session_id: str) -> dict:
"""
使用 LangChain 的 ConversationBufferMemory 进行对话
参数:
message: 用户消息
session_id: 会话ID
返回:
字典,包含:
- response (str): AI回复
- memory_variables (dict): ConversationBufferMemory 的内部变量
实现要求:
1. 使用 ConversationBufferMemory 管理每个 session 的历史
2. 将 Memory 对象与 Ollama LLM 集成
3. memory_variables 应包含 'history' 键
4. 不同 session 的 Memory 必须独立
"""
global SESSION_MEMORIES
# 1. 检查 session_id 是否存在对应的 Memory,不存在则创建
if session_id not in SESSION_MEMORIES:
SESSION_MEMORIES[session_id] = ConversationBufferMemory(return_messages=True)
# 2. 创建 Ollama LLM 实例
llm = Ollama(
model="qwen3:0.6b",
base_url="http://localhost:11434"
)
# 3. 创建 PromptTemplate(包含历史上下文)
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["input", "history"],
template="下面是之前的对话历史:\n{history}\n\n用户:{input}\n\n助手:"
)
# 获取当前会话的 Memory
memory = SESSION_MEMORIES[session_id]
# 4. 创建 LLMChain,连接 Prompt、LLM 和 Memory
chain = LLMChain(
llm=llm,
prompt=prompt,
memory=memory
)
# 5. 运行链并获取响应
try:
result = chain.invoke({
"input": message,
"history": memory.buffer if hasattr(memory, 'buffer') else ""
})
response = result.get("text", "") if isinstance(result, dict) else str(result)
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"运行LLMChain时发生错误: {e}")
# 6. 返回响应和 memory_variables
# ConversationBufferMemory 没有 variables 属性,需要构造一个包含 history 的字典
memory_variables = {
"history": memory.buffer
}
return {
"response": response,
"memory_variables": memory_variables
}
def get_memory_summary(session_id: str) -> str:
"""
获取指定会话的完整历史记录摘要
参数:
session_id: 会话ID
返回:
格式化的历史记录字符串,如:
"User: 你好\nAI: 你好!有什么可以帮助你的吗?\nUser: ..."
如果会话不存在,返回空字符串或提示信息
实现要求:
1. 返回人类可读的格式
2. 包含完整的用户输入和AI回复
3. 对不存在的 session_id,返回空字符串或提示
"""
global SESSION_MEMORIES
# 1. 检查 session_id 是否存在
if session_id not in SESSION_MEMORIES:
return ""
# 获取当前会话的 Memory
memory = SESSION_MEMORIES[session_id]
# 2. 获取 Memory 的 buffer 或 chat_memory
history_messages = memory.buffer if hasattr(memory, 'buffer') else []
# 3. 格式化消息历史为可读字符串
formatted_history = []
if history_messages:
for message in history_messages:
# 处理消息对象
if hasattr(message, 'type'):
# 消息对象有 type 属性
if message.type == 'human':
formatted_history.append(f"User: {message.content}")
elif message.type == 'ai':
formatted_history.append(f"AI: {message.content}")
elif isinstance(message, dict):
# 消息是字典格式
role = message.get('role', '')
content = message.get('content', '')
if role in ['user', 'human', 'User', 'user']:
formatted_history.append(f"User: {content}")
elif role in ['assistant', 'ai', 'Assistant', 'assistant']:
formatted_history.append(f"AI: {content}")
else:
# 其他情况,转换为字符串
formatted_history.append(str(message))
# 4. 返回格式化结果
return "\n".join(formatted_history)
def clear_memory(session_id: str = None):
"""
清除会话记忆(辅助函数,用于测试)
参数:
session_id: 要清除的会话ID,如果为 None 则清除所有会话
"""
global SESSION_MEMORIES
if session_id is None:
SESSION_MEMORIES.clear()
elif session_id in SESSION_MEMORIES:
del SESSION_MEMORIES[session_id]
# 测试代码(可选,用于学生本地调试)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 清空记忆
clear_memory()
# 测试对话
print("=== 测试 LangChain Memory ===")
session_id = "test_session"
result1 = chat_with_langchain_memory("我的电话是13800138000", session_id)
print(f"第1次对话:")
print(f" Response: {result1['response'][:50]}")
print(f" Memory variables keys: {result1['memory_variables'].keys()}")
result2 = chat_with_langchain_memory("我的邮箱是test@example.com", session_id)
print(f"\n第2次对话:")
print(f" Response: {result2['response'][:50]}")
# 获取历史摘要
summary = get_memory_summary(session_id)
print(f"\n历史摘要:\n{summary}")
# 验证信息是否保存
print(f"\n验证信息持久化:")
print(f" 包含电话号码: {'13800138000' in summary}")
print(f" 包含邮箱: {'test@example.com' in summary}")2. 运行结果
python .\main.py【例】
D:\sumu_blog\python-ai\lab3> python .\main.py
=== 测试 LangChain Memory ===
D:\sumu_blog\python-ai\lab3\main.py:55: LangChainDeprecationWarning: The class `LLMChain` was deprecated in LangChain 0.1.17 and will be removed in 1.0. Use RunnableSequence, e.g., `prompt | llm` instead.
chain = LLMChain(
第1次对话:
Response: 您好!请问您需要拨打电话吗?如果需要,请告诉我您的姓名或问题,我会帮您处理。
Memory variables keys: dict_keys(['history'])
第2次对话:
Response: 您好!请问您需要拨打电话吗?如果需要,请告诉我您的姓名或问题,我会帮您处理。您目前的邮箱是test@
历史摘要:
User: 我的电话是13800138000
AI: 您好!请问您需要拨打电话吗?如果需要,请告诉我您的姓名或问题,我会帮您处理。
User: 我的邮箱是test@example.com
AI: 您好!请问您需要拨打电话吗?如果需要,请告诉我您的姓名或问题,我会帮您处理。您目前的邮箱是test@example.com,有什么需要帮助的吗?
验证信息持久化:
包含电话号码: True
包含邮箱: True