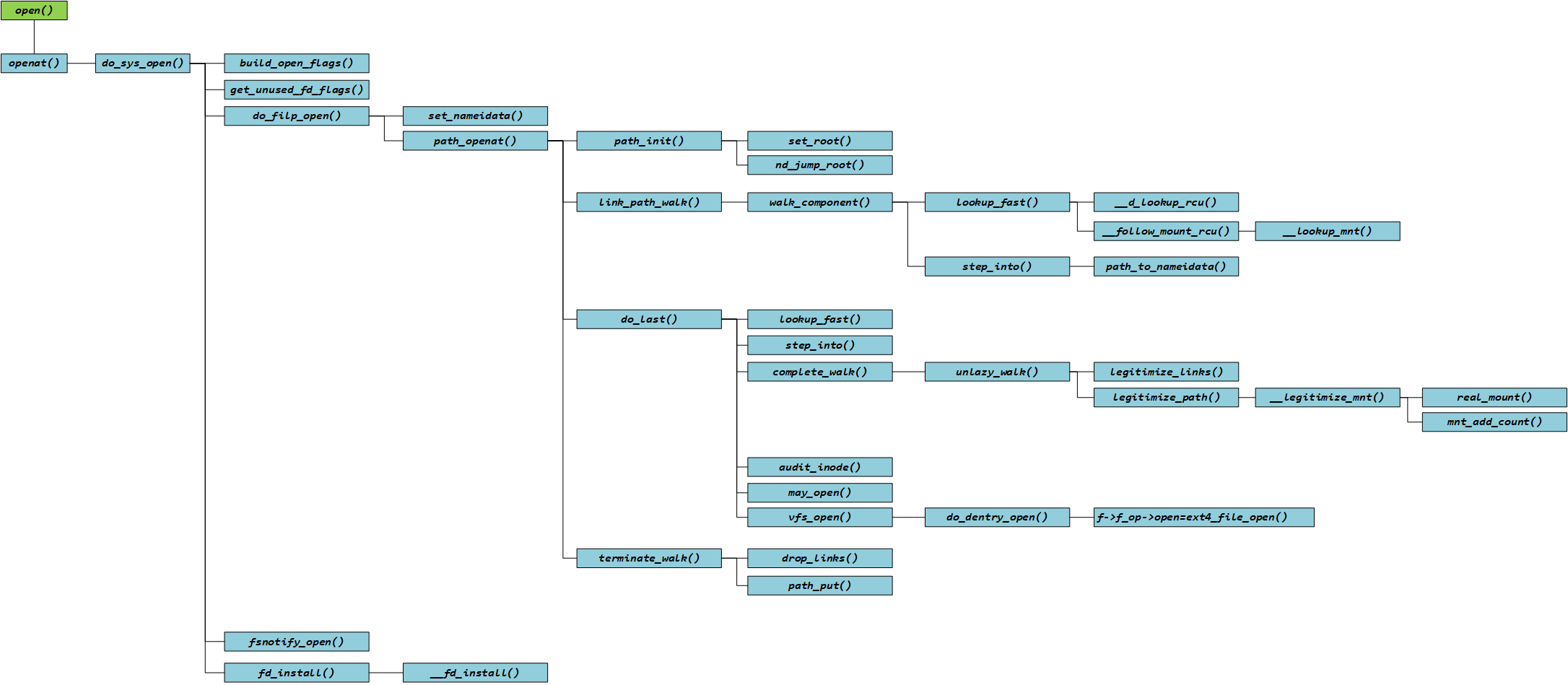
LV202-open函数解析2
本文主要是 kernel——open 函数系统调用过程中,dentry 结构的创建以及如何通过 inode 查找和关联的过程。从 d_alloc_parallel()开始,经 d_alloc()、__d_alloc()函数,最终在 ext4_lookup()中找到 inode,并在 d_splice_alias()和__d_add()函数中完成 dentry 与 inode 的绑定,确保后续 lookup 快速定位。
一、open 函数调用回顾
这里还是先以打开前面的 demo 为例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int fd = open("/home/sumu/7Linux/test.txt", O_CREAT | O_RDWR);
close(fd);
return 0;
}回顾一下 open 函数的调用过程:
在《01 嵌入式开发/02IMX6ULL 平台/LV05-系统镜像/LV05-03-Kernel-05-03-02-open 函数解析 1.md》里面我们以打开 "/home/sumu/7Linux/test.txt" 为例分析了系统调用 "open" 的内核实现。其中我们假设了路径名中所有部分的 dentry 结构体均已存在在系统缓存中。即通过 lookup_fast() 函数成功找到目标文件的 dentry。那要是这个函数调用失败了,没有找到目标文件的 dentry 怎么办?这一节就来分析一下吧。
二、walk_component()分析
我们直接来到 walk_component() 函数中:
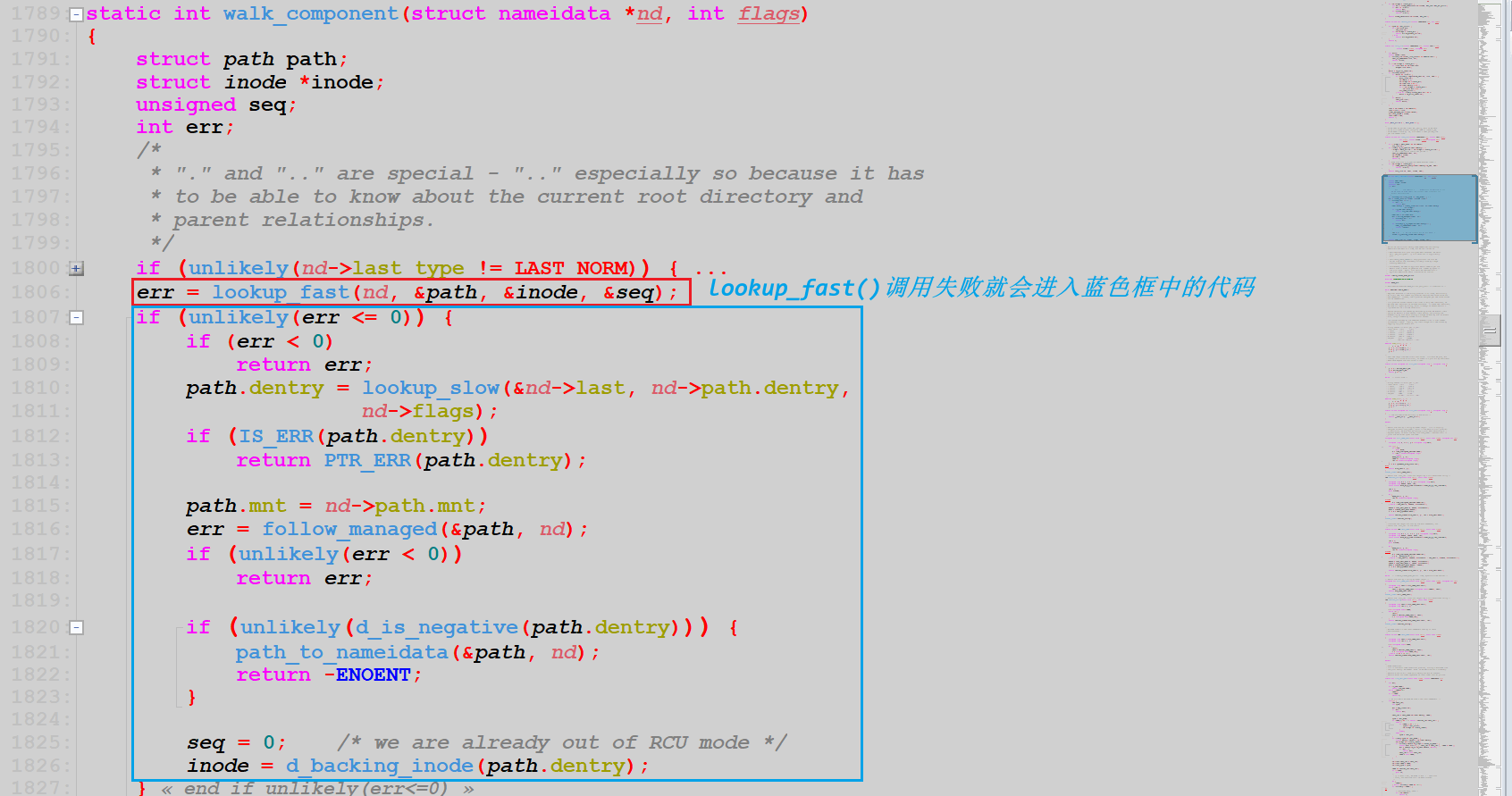
在 walk_component() 函数通过调用 lookup_fast() 函数失败时,进入 lookup_slow() 函数。在 lookup_slow() 函数为目标文件创建一个新的 dentry,并加入到系统缓存中。现来分析其具体过程,例如假设文件夹“sumu”尚不存在在系统缓存中(虽然这种情况几乎不存在)。
说明:在这里我们仍然不考虑函数调用失败和进程同步等问题)
1. lookup_slow()
lookup_slow() 函数定义如下:
static struct dentry *lookup_slow(const struct qstr *name,
struct dentry *dir,
unsigned int flags)
{
struct inode *inode = dir->d_inode;
struct dentry *res;
inode_lock_shared(inode);
res = __lookup_slow(name, dir, flags);
inode_unlock_shared(inode);
return res;
}可以看到 lookup_slow() 函数内部调用了 [__lookup_slow()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/namei.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n1642) 函数:
/* Fast lookup failed, do it the slow way */
static struct dentry *__lookup_slow(const struct qstr *name,
struct dentry *dir,
unsigned int flags)
{
struct dentry *dentry, *old;
struct inode *inode = dir->d_inode;
DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD_ONSTACK(wq);
/* Don't go there if it's already dead */
if (unlikely(IS_DEADDIR(inode))) // if 判断为 0
//......
again:
dentry = d_alloc_parallel(dir, name, &wq);
if (IS_ERR(dentry)) // if 判断为 0
//......
if (unlikely(!d_in_lookup(dentry))) { // 不考虑并发性问题, if 判断为 0
//......
} else {
old = inode->i_op->lookup(inode, dentry, flags);// 一般情况下,返回 NULL
d_lookup_done(dentry);
if (unlikely(old)) { // if 判断为 0
//......
}
}
return dentry;
}1.1 d_alloc_parallel()
先来分析其中的 d_alloc_parallel() 函数。在我们分析的这种情况下,该函数定义等价与如下,(该函数涉及很多并发性问题的考虑,参考 《Parallel pathname lookups and the importance of testing》 ):
struct dentry *d_alloc_parallel(struct dentry *parent,
const struct qstr *name,
wait_queue_head_t *wq)
{
unsigned int hash = name->hash;
struct hlist_bl_head *b = in_lookup_hash(parent, hash);
struct hlist_bl_node *node;
struct dentry *new = d_alloc(parent, name);
struct dentry *dentry;
unsigned seq, r_seq, d_seq;
if (unlikely(!new)) // if 判断为 0
//......
retry:
rcu_read_lock();
seq = smp_load_acquire(&parent->d_inode->i_dir_seq);
r_seq = read_seqbegin(&rename_lock);
dentry = __d_lookup_rcu(parent, name, &d_seq);
if (unlikely(dentry)) { // if 判断为 0(dentry 刚刚被创建和初始化,但尚未被加入哈希表中 (不考虑并发性问题))
//......
}
if (unlikely(read_seqretry(&rename_lock, r_seq))) {// 暂不考虑并发性问题,假设此时无需 retry, if 判断为 0
//......
}
if (unlikely(seq & 1)) {
rcu_read_unlock();
goto retry;
}
hlist_bl_lock(b);
if (unlikely(READ_ONCE(parent->d_inode->i_dir_seq) != seq)) { // 暂不考虑,假设 if 判断为 0
//......
}
/*
* No changes for the parent since the beginning of d_lookup().
* Since all removals from the chain happen with hlist_bl_lock(),
* any potential in-lookup matches are going to stay here until
* we unlock the chain. All fields are stable in everything
* we encounter.
*/
// 遍历 in_lookup_hashtable,在不考虑并发性的问题情况下,新创建的这个 dentry 在 in_lookup_hashtable 中也找不到
hlist_bl_for_each_entry(dentry, node, b, d_u.d_in_lookup_hash) {
if (dentry->d_name.hash != hash) //if 判断始终为 1, 直到整个遍历结束
continue;
//......
}
rcu_read_unlock();
/* we can't take -> d_lock here; it's OK, though. */
new->d_flags |= DCACHE_PAR_LOOKUP;
new->d_wait = wq;
// 将新创建的 dentry 加入到 in_lookup_hashtable 中,以便并发访问的其他程序能够找到,不会重复创建相同 dentry
hlist_bl_add_head_rcu(&new->d_u.d_in_lookup_hash, b);
hlist_bl_unlock(b);
return new; // 函数返回
mismatch:
//......
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(d_alloc_parallel);1.1.1 d_alloc()
先看 d_alloc() 函数。在目前分析的情况下该函数等价如下:
/**
* d_alloc - allocate a dcache entry
* @parent: parent of entry to allocate
* @name: qstr of the name
*
* Allocates a dentry. It returns %NULL if there is insufficient memory
* available. On a success the dentry is returned. The name passed in is
* copied and the copy passed in may be reused after this call.
*/
struct dentry *d_alloc(struct dentry * parent, const struct qstr *name)
{
struct dentry *dentry = __d_alloc(parent->d_sb, name);
if (!dentry)
return NULL;
spin_lock(&parent->d_lock);
/*
* don't need child lock because it is not subject
* to concurrency here
*/
__dget_dlock(parent);
dentry->d_parent = parent;
list_add(&dentry->d_child, &parent->d_subdirs);//将新创建的 dentry-> d_child 加入 父目录的 dentry-> d_subdirs 链后面,此处不做详细分析
spin_unlock(&parent->d_lock);
return dentry;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(d_alloc);1.1.2 __d_alloc()
看一下 d_alloc() 中的[__d_alloc()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/dcache.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n1594) 函数,在这里分析如下:
struct dentry *__d_alloc(struct super_block *sb, const struct qstr *name)
{
struct external_name *ext = NULL;
struct dentry *dentry;
char *dname;
int err;
dentry = kmem_cache_alloc(dentry_cache, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dentry)
return NULL;
/*
* We guarantee that the inline name is always NUL-terminated.
* This way the memcpy() done by the name switching in rename
* will still always have a NUL at the end, even if we might
* be overwriting an internal NUL character
*/
dentry->d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN-1] = 0;
if (unlikely(!name)) {//这里 if 判断结果为 0
//......
} else if (name->len > DNAME_INLINE_LEN-1) {//DNAME_INLINE_LEN = 32, name ~ sumu/7Linux/test.txt, if 判断为 0
//......
} else {
dname = dentry->d_iname;
}
dentry->d_name.len = name->len;
dentry->d_name.hash = name->hash;
memcpy(dname, name->name, name->len);
dname[name->len] = 0;
/* Make sure we always see the terminating NUL character */
smp_store_release(&dentry->d_name.name, dname); /* ^^^ */
// 到这里,由于 name-> len 小于 dentry-> d_iname 数组的大小,因此 dentry-> d_iname 和 dentry-> d_name 指向的是同一个名字(sumu/7Linux/test.txt)
//下面是根据参数 struct qstr *name 和 struct super_block * sb 提供的信息初始化刚刚创建的 dentry
dentry->d_lockref.count = 1;
dentry->d_flags = 0;
spin_lock_init(&dentry->d_lock);
seqcount_init(&dentry->d_seq);
dentry->d_inode = NULL; // 注意,d_inode 没有赋值,整个 dentry 只能算是个空壳...
dentry->d_parent = dentry;
dentry->d_sb = sb;
dentry->d_op = NULL;
dentry->d_fsdata = NULL;
INIT_HLIST_BL_NODE(&dentry->d_hash);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dentry->d_lru);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dentry->d_subdirs);
INIT_HLIST_NODE(&dentry->d_u.d_alias);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dentry->d_child);
d_set_d_op(dentry, dentry->d_sb->s_d_op); // 在本例中 dentry-> d_op = sb-> s_d_op (== NULL)
if (dentry->d_op && dentry->d_op->d_init) { // dentry-> d_op == 0
//......
}
if (unlikely(ext)) {
pg_data_t *pgdat = page_pgdat(virt_to_page(ext));
mod_node_page_state(pgdat, NR_INDIRECTLY_RECLAIMABLE_BYTES,
ksize(ext));
}
this_cpu_inc(nr_dentry);
return dentry;
}可见,在 [__d_alloc()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/dcache.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n1594) 函数中,创建新的 struct dentry,并根据 父目录的 dentry→ d_sb 和本目录的 name 进行相关初始化。该函数返回之后,我们回到 [d_alloc()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/dcache.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n1684) 函数。在 [d_alloc()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/dcache.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n1684) 函数调用完毕 [__d_alloc()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/dcache.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n1594) 函数之后,再对新创建的 dentry 进行简单设置之后便返回了,详见上面代码部分。
1.1.3 总结
d_alloc() 函数结束之后返回到 d_alloc_parallel() 函数。d_alloc_parallel() 函数执行完 d_alloc() 函数之后,进行简单操作(不考虑并发性问题的考虑)之后,返回新创建的 dentry。d_alloc_parallel() 函数返回之后,便回到[__lookup_slow()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/namei.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n1642) 函数。
1.2 ext4_lookup()
需要注意的是,在整个 d_alloc_parallel() 函数中,只是创建了一个新的 dentry,但还没找到相应的 inode,整个 dentry 目前只是一具空壳。下面将进入 inode→ i_op→ lookup() 函数,在这个函数中,将找到相应的 inode,并与 dentry 联系起来。这是一个函数指针,要分析该函数需知道该指针指向的函数。其实该指针指向的是 ext4_lookup() 函数。为什么?其实这个函数根据不同文件系统指向不同的函数,但是大概都叫 xxx_lookup(),我们可以在 fs - kernel/git/stable/linux.git - Linux kernel stable tree 目录中搜索一下:
grep -nRw "lookup" ./fs/就会找到,若是 ext4 文件系统的话,就会指向这个 ext4_lookup() 函数,该函数定义如下:
static struct dentry *ext4_lookup(struct inode *dir, struct dentry *dentry, unsigned int flags)
{
struct inode *inode;
struct ext4_dir_entry_2 *de;
struct buffer_head *bh;
int err;
err = fscrypt_prepare_lookup(dir, dentry, flags);
if (err) // if 判断为 0
//......
if (dentry->d_name.len > EXT4_NAME_LEN) // if 判断为 0
//......
/***** **** 根据父目录和目标文件的文件名,找到目标文件的 inode **** *****/
bh = ext4_find_entry(dir, &dentry->d_name, &de, NULL);
if (IS_ERR(bh))
return (struct dentry *) bh;
inode = NULL;
if (bh) {
__u32 ino = le32_to_cpu(de->inode);
brelse(bh);
if (!ext4_valid_inum(dir->i_sb, ino)) {
EXT4_ERROR_INODE(dir, "bad inode number: %u", ino);
return ERR_PTR(-EFSCORRUPTED);
}
if (unlikely(ino == dir->i_ino)) {
EXT4_ERROR_INODE(dir, "'%pd' linked to parent dir",
dentry);
return ERR_PTR(-EFSCORRUPTED);
}
inode = ext4_iget(dir->i_sb, ino, EXT4_IGET_NORMAL);
if (inode == ERR_PTR(-ESTALE)) {
EXT4_ERROR_INODE(dir,
"deleted inode referenced: %u",
ino);
return ERR_PTR(-EFSCORRUPTED);
}
if (!IS_ERR(inode) && ext4_encrypted_inode(dir) &&
(S_ISDIR(inode->i_mode) || S_ISLNK(inode->i_mode)) &&
!fscrypt_has_permitted_context(dir, inode)) {
ext4_warning(inode->i_sb,
"Inconsistent encryption contexts: %lu/%lu",
dir->i_ino, inode->i_ino);
iput(inode);
return ERR_PTR(-EPERM);
}
}
/***** **** **** **** **** **** **** **** **** **** **** **** **** **** **** ******/
return d_splice_alias(inode, dentry);
}可见这个函数中大部分代码是用来找到目标文件的 inode。因为在前面的代码中,只是创建了一个 dentry 的“空壳”,还没有与任何一个 inode 相关联,这个 dentry 的 d_inode 被初始化为 dentry→ d_inode = NULL。在 ext4_lookup() 这个函数中找到对应的 inode。这也符合这个函数的名字:lookup, 就是要找到 inode。这里寻找 inode 的过程依赖 ext4 文件系统的配置和技术细节,这里将不进行深入分析了。
1.2.1 d_splice_alias()
而在这个函数的最后一部分,d_splice_alias() 函数中,将新创建的 dentry 与找到的 inode 进行关联,并顺便将新的 dentry 加入到哈希表中,这样下次执行 lookup_fast() 函数时,即可迅速找到可用的 dentry。下面看 d_splice_alias() 函数的定义:
struct dentry *d_splice_alias(struct inode *inode, struct dentry *dentry)
{
if (IS_ERR(inode))
return ERR_CAST(inode);
BUG_ON(!d_unhashed(dentry));
if (!inode)
goto out;
security_d_instantiate(dentry, inode);// 暂不分析该函数,可认为该函数什么都不做
spin_lock(&inode->i_lock);
if (S_ISDIR(inode->i_mode)) { // 判断是否为文件夹,if 判断为 1
struct dentry *new = __d_find_any_alias(inode);//我们只考虑最简单的情况,一般情况下 new == NULL
if (unlikely(new)) {//一般情况下, if 判断为 0
//......
}
}
out:
__d_add(dentry, inode);
return NULL;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(d_splice_alias);可见,这个函数里面只调用了[__d_add()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/dcache.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n2561) 函数。该函数定义如下:
static inline void __d_add(struct dentry *dentry, struct inode *inode)
{
struct inode *dir = NULL;
unsigned n;
spin_lock(&dentry->d_lock);
if (unlikely(d_in_lookup(dentry))) { // 此处 if 判断为 1,但这里我们并不做具体分析
dir = dentry->d_parent->d_inode;
n = start_dir_add(dir);
__d_lookup_done(dentry);
}
if (inode) { // if 判断为 1
unsigned add_flags = d_flags_for_inode(inode);
hlist_add_head(&dentry->d_u.d_alias, &inode->i_dentry);
raw_write_seqcount_begin(&dentry->d_seq);
__d_set_inode_and_type(dentry, inode, add_flags); // 设置 dentry 的 inode 和 flags
raw_write_seqcount_end(&dentry->d_seq);
fsnotify_update_flags(dentry);
}
__d_rehash(dentry); // 此时新创建的 dentry 已经完全可用,将其加入到 哈希表 中
if (dir) // if 判断为 1,但此处不做分析
end_dir_add(dir, n);
spin_unlock(&dentry->d_lock);
if (inode)
spin_unlock(&inode->i_lock);
}可见,在这个函数中,最终设置了 dentry 的 inode,并将其加入到哈希表中,如此一来,下次可直接通过 lookup_fast() 函数找到该 dentry。
1.2.2 总结
[__d_add()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/dcache.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n2561) 函数返回后,回到 [d_splice_alias()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/dcache.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n2897) 函数,之后又返回到 [ext4_lookup()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/ext4/namei.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n1560) 函数,之后又返回到 [__lookup_slow()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/namei.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n1642) 函数, [__lookup_slow()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/namei.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n1642) 函数紧接着调用 [lookup_done()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/include/linux/dcache.h?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n364) 函数,这个函数只是处理并发性问题,这里我们不考虑,可以认为该函数什么都没做。在这之后, [__lookup_slow()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/namei.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n1642) 函数返回至 [lookup_slow()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/namei.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n1681) 函数,然后继续返回到 [walk_component()](https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git/tree/fs/namei.c?h = v4.19.71&id = e7d2672c66e4d3675570369bf20856296da312c4#n1789) 函数,后面执行的操作和我们所《01 嵌入式开发/02IMX6ULL 平台/LV05-系统镜像/LV05-03-Kernel-05-03-02-open 函数解析 1.md》里面分析的一样。
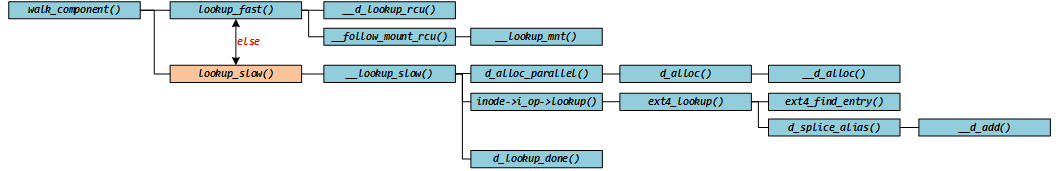
三、 lookup_open()
注意,如果是路径名的最后一部分不在 dcache 中,那么创建 dentry 以及查找 inode 的操作不在 lookup_slow() 函数中进行,而是在 do_last() 函数中,通过调用 lookup_open() 函数来完成,调用的部分在这一行 do_last() → lookup_open() 与上述过程略有不同,但基本过程是一样的,这里就不详细去分析了。
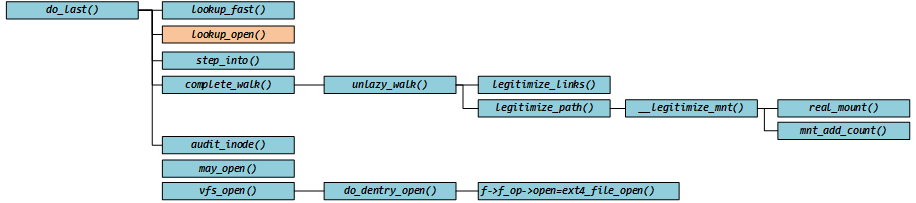
四、总结
分析到现在,我们对 open 的分析涉及到这些函数了:
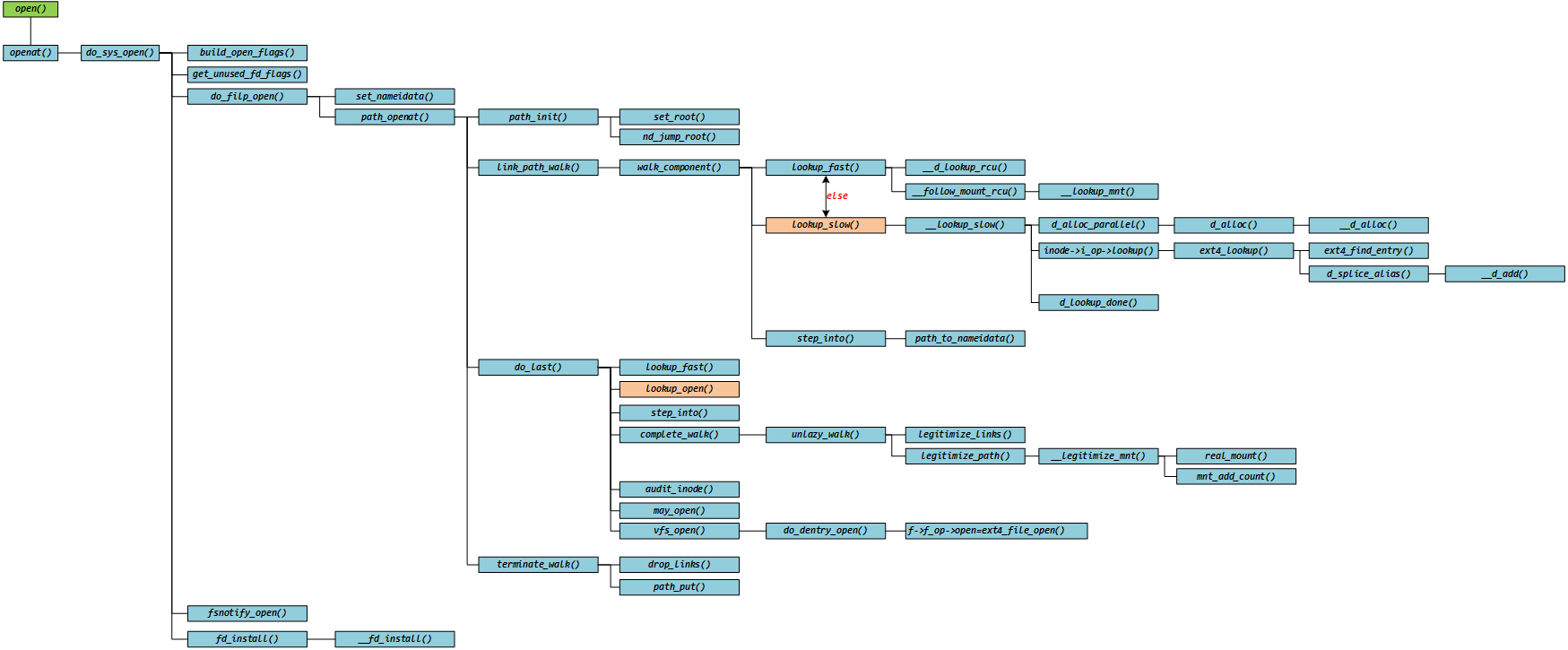
参考资料
Linux 中 open 命令实现原理以及源码分析_linux open-CSDN 博客
linux 文件描述符分配实现详解(基于 ARM 处理器)_fdtable-CSDN 博客