LV035-触摸屏应用实例
一、获取触摸屏点数
1. 代码编写
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
// /proc/bus/input/devices 命令查看输入事件
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct input_absinfo info;
int fd = -1;
int max_slots;
/* 校验传参 */
if (2 != argc)
{
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s <input-dev>\n", argv[0]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
/* 打开文件 */
if (0 > (fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY)))
{
perror("open error");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
/* 获取 slot 信息 */
if (0 > ioctl(fd, EVIOCGABS(ABS_MT_SLOT), &info))
{
perror("ioctl error");
close(fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
max_slots = info.maximum + 1 - info.minimum;
printf("max_slots: %d\n", max_slots);
/* 关闭、退出 */
close(fd);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}2. 开发板测试
shell
cat /proc/bus/input/devices
./app_demo /dev/input/event1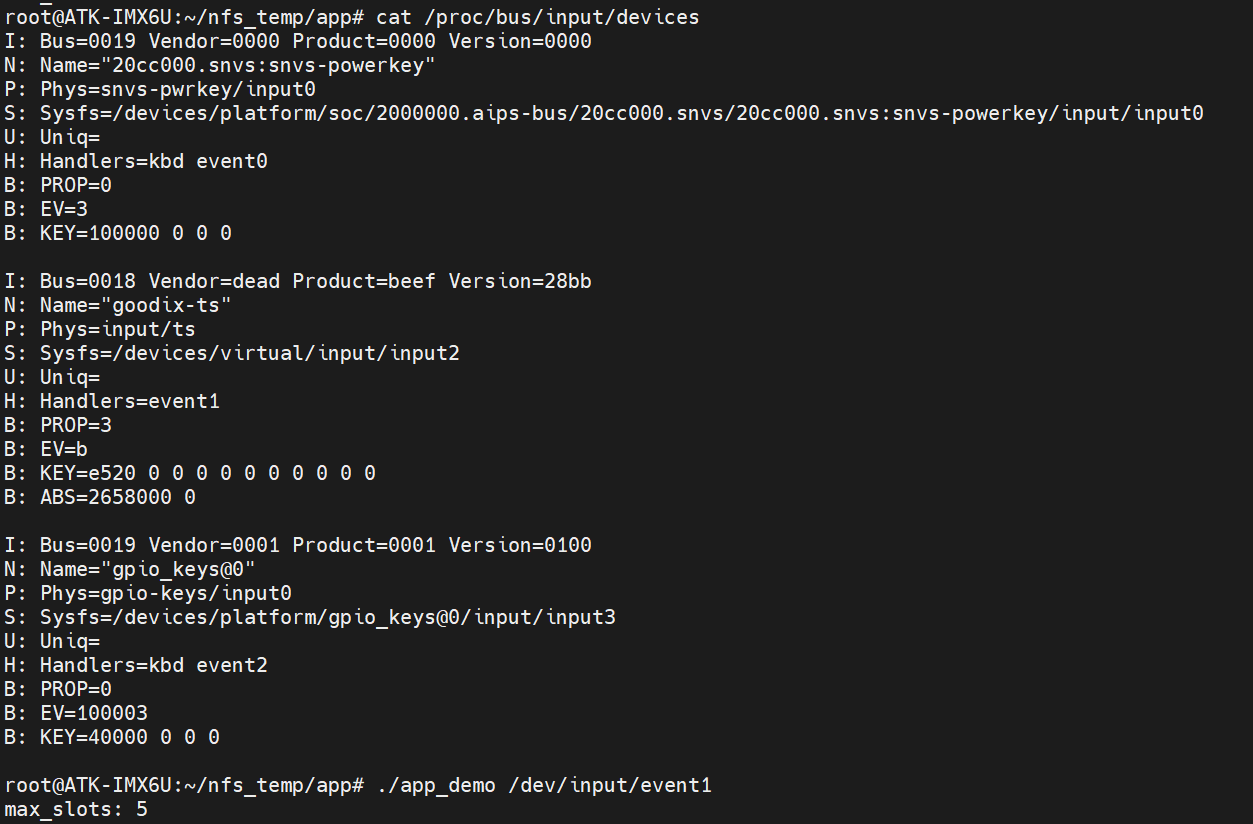
可以看到这个是一个 5 点的触摸屏。
二、单点触摸
这里我的触摸屏好像并不会上报按下的这个事件,所以流程与多点触摸一致了,直接看多点触摸的实例。
三、多点触摸
1. 代码编写
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
/* 用于描述 MT 多点触摸每一个触摸点的信息 */
struct ts_mt
{
int x; //X 坐标
int y; //Y 坐标
int id; //对应 ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID
int valid; //数据有效标志位(= 1 表示触摸点信息发生更新)
};
/* 一个触摸点的 x 坐标和 y 坐标 */
struct tp_xy
{
int x;
int y;
};
static int ts_read(const int fd, const int max_slots, struct ts_mt *mt)
{
struct input_event in_ev = {{0}};
static int slot = 0;//用于保存上一个 slot
static struct tp_xy xy[12] = {{0}};//用于保存上一次的 x 和 y 坐标值, 假设触摸屏支持的最大触摸点数不会超过 12
int i = 0;
/* 对缓冲区初始化操作 */
memset(mt, 0x0, max_slots * sizeof(struct ts_mt)); //清零
for (i = 0; i < max_slots; i++)
{
mt[i].id = -2;//将 id 初始化为-2, id =-1 表示触摸点删除, id >= 0 表示创建
}
while(1)
{
if (sizeof(struct input_event) != read(fd, &in_ev, sizeof(struct input_event)))
{
perror("read error");
return -1;
}
#if 1
printf("[INFO]event type:%d code:%d value:%d\n", in_ev.type, in_ev.code, in_ev.value);
#endif
switch (in_ev.type)
{
case EV_ABS:
switch (in_ev.code)
{
case ABS_MT_SLOT:
slot = in_ev.value;
break;
case ABS_MT_POSITION_X:
xy[slot].x = in_ev.value;
mt[slot].valid = 1;
break;
case ABS_MT_POSITION_Y:
xy[slot].y = in_ev.value;
mt[slot].valid = 1;
break;
case ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID:
mt[slot].id = in_ev.value;
mt[slot].valid = 1;
break;
default:
break;
}
break;
//case EV_KEY://按键事件对单点触摸应用比较有用
// break;
case EV_SYN:
if (SYN_REPORT == in_ev.code)
{
for (i = 0; i < max_slots; i++)
{
mt[i].x = xy[i].x;
mt[i].y = xy[i].y;
}
}
return 0;
default:
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
// /proc/bus/input/devices 命令查看输入事件
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct input_absinfo slot = {0};
struct ts_mt *mt = NULL;
int max_slots = 0;
int fd = -1;
int i = 0;
/* 校验传参 */
if (2 != argc)
{
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s <input-dev>\n", argv[0]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
/* 打开文件 */
if (0 > (fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY)))
{
perror("open error");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
/* 获取触摸屏支持的最大触摸点数 */
if (0 > ioctl(fd, EVIOCGABS(ABS_MT_SLOT), &slot))
{
perror("ioctl error");
close(fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
max_slots = slot.maximum + 1 - slot.minimum;
printf("max_slots: %d\n", max_slots);
/* 申请内存空间并清零 */
mt = calloc(max_slots, sizeof(struct ts_mt));
/* 读数据 */
while(1)
{
if (0 > ts_read(fd, max_slots, mt))
{
break;
}
for (i = 0; i < max_slots; i++)
{
if (mt[i].valid)
{
//判断每一个触摸点信息是否发生更新(关注的信息发生更新)
if (0 <= mt[i].id)
printf("slot<%d>, press(%d, %d)\n", i, mt[i].x, mt[i].y);
else if (-1 == mt[i].id)
printf("slot<%d>, lift\n", i);
else
printf("slot<%d>, move(%d, %d)\n", i, mt[i].x, mt[i].y);
}
}
}
/* 关闭设备、退出 */
close(fd);
free(mt);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}示例代码中定义了 struct ts_mt 数据结构,用于描述多点触摸情况下每一个触摸点的信息。
首先来看下 main()函数,定义了 max_slots 变量,用于指定触摸屏设备的支持的最大触摸点数,通过:
c
ioctl(fd, EVIOCGABS(ABS_MT_SLOT), &slot)获取到触摸屏该信息。
接着根据 max_slots 变量的值,为 mt 指针申请内存:
c
mt = calloc(max_slots, sizeof(struct ts_mt));while 循环中调用 ts_read()函数,该函数是自定义函数,用于获取触摸屏上报的数据, 第一个参数表示文件描述符 fd、第二个参数表示触摸屏支持的最大触摸点数、第三个参数则是 struct ts_mt 数组, ts_read()函数会将获取到的数据存放在数组中, mt[0]表示 slot < 0 > 数据、 mt[1]表示 slot < 1 > 的数据依次类推。
在内部的 for 循环中,则对获取到的数据进行分析,判断数据是否有效,并根据 id 判断手指的动作,在单点触摸应用程序中,我们是通过 BTN_TOUCH 事件来判断手指的动作;而在多点触摸应用中,我们需要通过 id 来判断多个手指的动作。
2. 开发板测试
我们编译后执行,然后多个手指按下的时候会有如下打印:
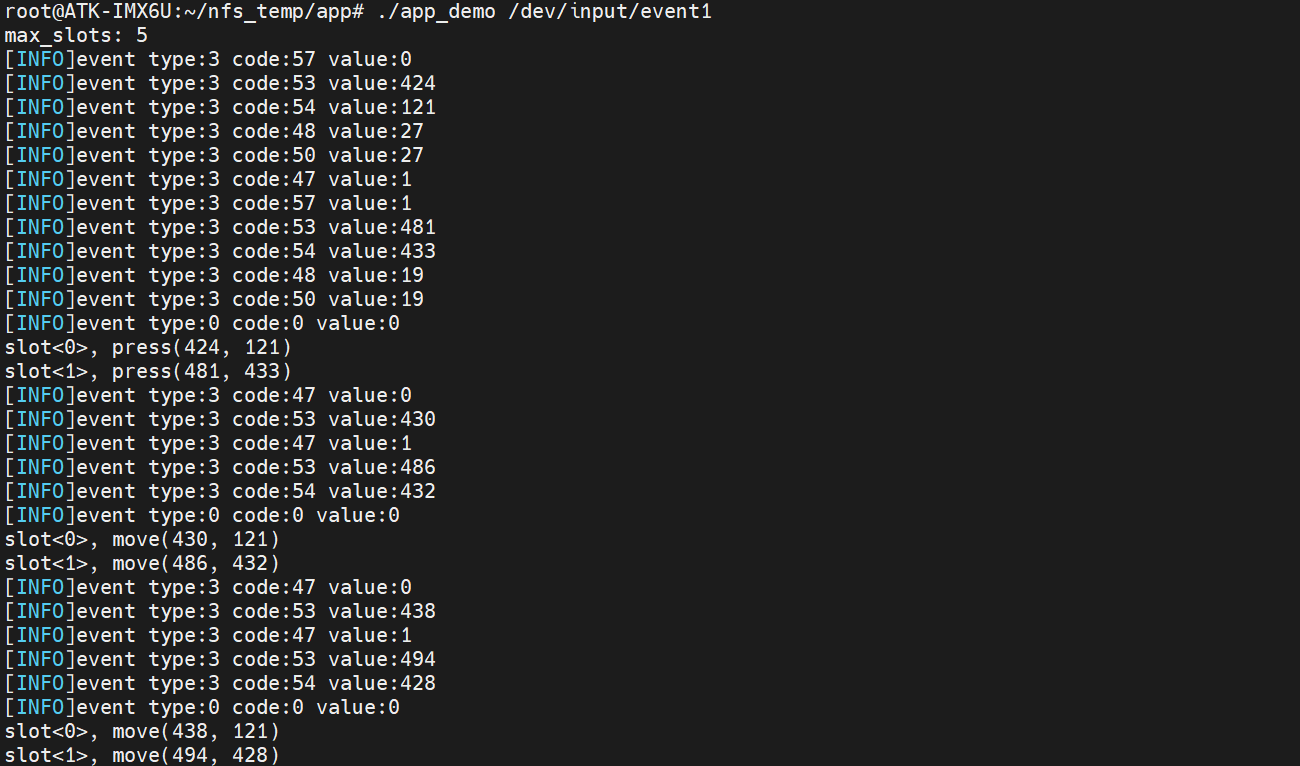
上图是按下和移动的打印信息,当手指拿开的时候如下:
