LV060-参数传递
我们编写 C 语言函数的时候,函数的传入参数,根据传入参数的不同我们可以实现不同的功能,就连执行 main 函数的时候也可以传输参数。
内核模块作为一个可拓展的动态模块,为 Linux 内核提供了灵活性,但是有时我们需要根据不同的应用场景给内核传递不同的参数, 例如在程序中开启调试模式、设置详细输出模式以及制定与具体模块相关的选项,都可以通过参数的形式来改变模块的行为。
一、怎么传递参数?
Linux 内核提供了以下几个宏来实现不同类型参数的传递:
- 基本类型:module_param(name, type, perm)
- 数组参数:module_param_array(name, type, nump, perm)
- 字符串参数:module_param_string(name, string, len, perm)
1. module_param
这个宏定义在 moduleparam.h - include/linux/moduleparam.h - module_param :
/**
* module_param - typesafe helper for a module/cmdline parameter
* @value: the variable to alter, and exposed parameter name.
* @type: the type of the parameter
* @perm: visibility in sysfs.
*
* @value becomes the module parameter, or (prefixed by KBUILD_MODNAME and a
* ".") the kernel commandline parameter. Note that - is changed to _, so
* the user can use "foo-bar = 1" even for variable "foo_bar".
*
* @perm is 0 if the the variable is not to appear in sysfs, or 0444
* for world-readable, 0644 for root-writable, etc. Note that if it
* is writable, you may need to use kernel_param_lock() around
* accesses (esp. charp, which can be kfreed when it changes).
*
* The @type is simply pasted to refer to a param_ops_##type and a
* param_check_##type: for convenience many standard types are provided but
* you can create your own by defining those variables.
*
* Standard types are:
* byte, short, ushort, int, uint, long, ulong
* charp: a character pointer
* bool: a bool, values 0/1, y/n, Y/N.
* invbool: the above, only sense-reversed (N = true).
*/
#define module_param(name, type, perm) \
module_param_named(name, name, type, perm)以上代码中的 module_param 函数需要传入三个参数:
name: 我们定义的变量名;
type: 参数的类型,目前内核支持的参数类型有 byte,short,ushort,int,uint,long,ulong,charp,bool,invbool。其中 short 表示短整型。ushort 表示无符号短整型 。int 表示整型 。uint 表示无符号整型。long 表示长整型。ulong 表示无符号长整型。charp 表示的是字符指针。bool 是布尔类型,其值只能为 0 或者是 1。invbool 是反布尔类型,其值也是只能取 0 或者是 1,但是 true 值表示 0,false 表示 1。变量是 char 类型时,传参只能是 byte,char * 时只能是 charp。
perm: 表示的是该文件的权限,具体参数值见下表。
| 用户组 | 标志位 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|
| 当前用户 | S_IRUSR | 用户拥有读权限 |
| S_IWUSR | 用户拥有写权限 | |
| 当前用户组 | S_IRGRP | 当前用户组的其他用户拥有读权限 |
| S_IWUSR | 当前用户组的其他用户拥有写权限 | |
| 其他用户 | S_IROTH | 其他用户拥有读权限 |
| S_IWOTH | 其他用户拥有写权限 |
上述文件权限唯独没有关于可执行权限的设置,请注意, 该文件不允许它具有可执行权限。如果强行给该参数赋予表示可执行权限的参数值 S_IXUGO, 那么最终生成的内核W模块在加载时会提示错误。其实参数 perm 在 sysfs 文件系统中所对应的文件节点的属性, 其权限定义在“stat.h - include/uapi/linux/stat.h”文件中。 可以用宏定义和数字法两种方式来表示:
#define S_IRWXU 00700
#define S_IRUSR 00400 /*文件所有者可读*/
#define S_IWUSR 00200 /*文件所有者可写*/
#define S_IXUSR 00100 /*文件所有者可执行*/
#define S_IRWXG 00070
#define S_IRGRP 00040 /*与文件所有者同组的用户可读*/
#define S_IWGRP 00020 /*与文件所有者同组的用户可写*/
#define S_IXGRP 00010 /*与文件所有者同组的用户可执行*/
#define S_IRWXO 00007
#define S_IROTH 00004 /*与文件所有者不同组的用户可读*/
#define S_IWOTH 00002 /*与文件所有者不同组的用户可写*/
#define S_IXOTH 00001 /*与文件所有者不同组的用户可可执行*/还有一些组合的定义在 stat.h - include/linux/stat.h:
#define S_IRWXUGO (S_IRWXU|S_IRWXG|S_IRWXO)
#define S_IALLUGO (S_ISUID|S_ISGID|S_ISVTX|S_IRWXUGO)
#define S_IRUGO (S_IRUSR|S_IRGRP|S_IROTH)
#define S_IWUGO (S_IWUSR|S_IWGRP|S_IWOTH)
#define S_IXUGO (S_IXUSR|S_IXGRP|S_IXOTH)2. module_param_array
module_param_array 定义在 moduleparam.h - include/linux/moduleparam.h - module_param_array:
/**
* module_param_array - a parameter which is an array of some type
* @name: the name of the array variable
* @type: the type, as per module_param()
* @nump: optional pointer filled in with the number written
* @perm: visibility in sysfs
*
* Input and output are as comma-separated values. Commas inside values
* don't work properly (eg. an array of charp).
*
* ARRAY_SIZE(@name) is used to determine the number of elements in the
* array, so the definition must be visible.
*/
#define module_param_array(name, type, nump, perm) \
module_param_array_named(name, name, type, nump, perm)可以使用 module_param_array 传递数组类型参数, 相较于 module_param ()函数多了 nump 参数, 用来表示传递参数个数,nump 参数值会根据输入的参数个数而改变,nump 的最终值为传递的数组元素个数。
3. module_param_string
module_param_string 用来传递字符串类型的变量 ,它定义在 moduleparam.h - include/linux/moduleparam.h - module_param_string :
/**
* module_param_string - a char array parameter
* @name: the name of the parameter
* @string: the string variable
* @len: the maximum length of the string, incl. terminator
* @perm: visibility in sysfs.
*
* This actually copies the string when it's set (unlike type charp).
* @len is usually just sizeof(string).
*/
#define module_param_string(name, string, len, perm) \
static const struct kparam_string __param_string_##name \
= { len, string }; \
__module_param_call(MODULE_PARAM_PREFIX, name, \
¶m_ops_string, \
.str = &__param_string_##name, perm, -1, 0);\
__MODULE_PARM_TYPE(name, "string")name:外部传入的参数名, 即加载模块时的传入值
string:内部的变量名, 即程序内定义的参数名
len:以 string 命名的 buffer 大小(可以小于 buffer 的大小, 但是没有意义)
perm:模块参数的访问权限 。
4. 头文件包含
上面的几个宏使用的时候需要包含 moduleparam.h - include/linux/moduleparam.h 文件,但是这个文件在已经在 module.h - include/linux/module.h 中进行了包含:
#ifndef _LINUX_MODULE_H
#define _LINUX_MODULE_H
/*
* Dynamic loading of modules into the kernel.
*
* Rewritten by Richard Henderson <rth@tamu.edu> Dec 1996
* Rewritten again by Rusty Russell, 2002
*/
// ......
#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
// ......
#endif /* _LINUX_MODULE_H */5. /sys/module/模块名/parameters
前面我们知道当模块初始化成功的时候会在/sys/module 下新建一个以模块名为名的目录。这里当模块带有参数的时候,会在 /sys/module/模块名 这个目录下创建一个名为 parameters 的目录,里面会显示我们在模块中定义的一些参数名。后面我们实际看一下就明白了。
二、参数传递实例
1. 代码实例
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h> /* module_init module_exit */
#include <linux/module.h> /* MODULE_LICENSE */
#include "./timestamp_autogenerated.h"
#include "./version_autogenerated.h"
static int number; // 定义 int 类型变量 number
static char *name; // 定义 char 类型变量 name
static int para[8]; // 定义 int 类型的数组
static char str1[10]; // 定义 char 类型字符串 str1
static int n_para; // 定义 int 类型的用来记录 module_param_array 函数传递数组元素个数的变量 n_para
module_param(number, int, S_IRUGO); // 传递 int 类型的参数 number,S_IRUGO 表示权限为可读
module_param(name, charp, S_IRUGO); // 传递 char 类型变量 name
module_param_array(para , int , &n_para , S_IRUGO); // 传递 int 类型的数组变量 para
module_param_string(str, str1 ,sizeof(str1), S_IRUGO); // 传递字符串类型的变量 str1
// 模块入口函数
static int __init module_param_demo_init(void)
{
int i = 0;
printk("*** [%s:%d]Build Time: %s %s, git version:%s ***\n", __FUNCTION__, __LINE__, KERNEL_KO_DATE, KERNEL_KO_TIME, KERNEL_KO_VERSION);
printk("module_param_demo module init!\n");
printk(KERN_EMERG "number=%d\n",number);
printk(KERN_EMERG "name=%s\n",name);
for(i = 0; i < n_para; i++)
{
printk(KERN_EMERG "para[%d] : %d \n", i, para[i]);
}
printk(KERN_EMERG "str1=%s\n",str1);
return 0;
}
// 模块出口函数
static void __exit module_param_demo_exit(void)
{
printk("module_param_demo exit!\n");
}
// 将__init 定义的函数指定为驱动的入口函数
module_init(module_param_demo_init);
// 将__exit 定义的函数指定为驱动的出口函数
module_exit(module_param_demo_exit);
/* 模块信息(通过 modinfo module_param_demo 查看) */
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); /* 源码的许可证协议 */
MODULE_AUTHOR("sumu"); /* 字符串常量内容为模块作者说明 */
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Description"); /* 字符串常量内容为模块功能说明 */
MODULE_ALIAS("module's other name"); /* 字符串常量内容为模块别名 */2. 开发板测试
2.1 不传参数
我们不传参试一下:
insmod module_param_demo.ko会看到如下打印信息:
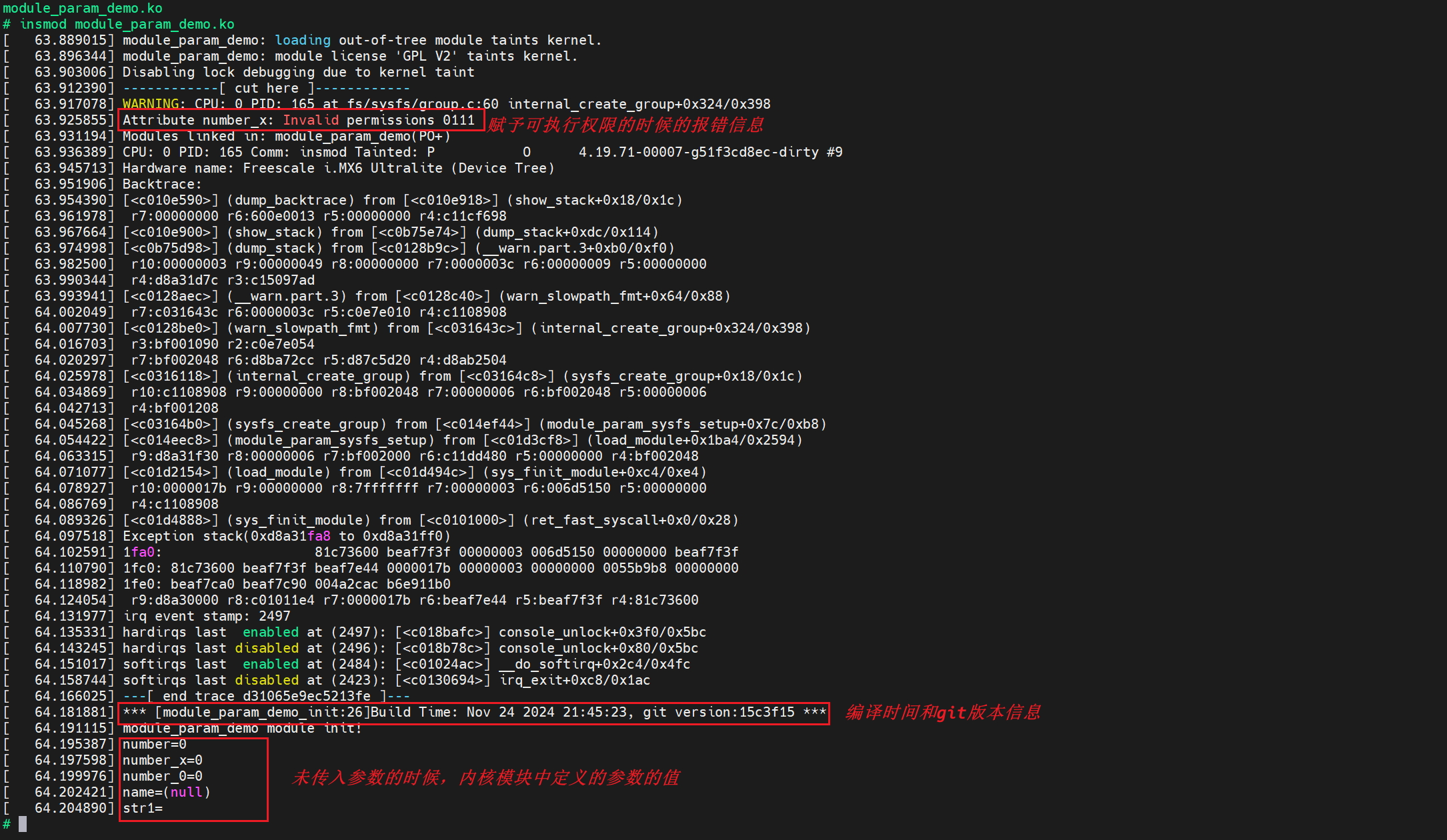
会发现出现了上面提到的报错信息,这个报错就是因为我们给了 number_x 这个参数可执行权限。另外会看到其他的参数都是 0,因为我们并没有传参进来。
2.2 传递参数
我们在串口终端敲以下命令:
insmod module_param_demo.ko number=10 number_x=11 number_0=12 name="sumu" para=0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 str="demo"我们将会看到以下输出信息:
# insmod module_param_demo.ko number = 10 number_x = 11 number_0 = 12 name = "sumu" para = 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 str = "demo"
[ 220.278258] ------------[ cut here ]------------
[ 220.283281] WARNING: CPU: 0 PID: 167 at fs/sysfs/group.c:60 internal_create_group+0x324/0x398
[ 220.291995] Attribute number_x: Invalid permissions 0111
[ 220.297346] Modules linked in: module_param_demo(PO+) [last unloaded: module_param_demo]
[ 220.305603] CPU: 0 PID: 167 Comm: insmod Tainted: P W O 4.19.71-00007-g51f3cd8ec-dirty #9
[ 220.314936] Hardware name: Freescale i.MX6 Ultralite (Device Tree)
[ 220.321139] Backtrace:
[ 220.323639] [<c010e590>] (dump_backtrace) from [<c010e918>] (show_stack+0x18/0x1c)
[ 220.331242] r7:00000000 r6:600f0013 r5:00000000 r4:c11cf698
[ 220.336939] [<c010e900>] (show_stack) from [<c0b75e74>] (dump_stack+0xdc/0x114)
[ 220.344289] [<c0b75d98>] (dump_stack) from [<c0128b9c>] (__warn.part.3+0xb0/0xf0)
[ 220.351805] r10:00000003 r9:00000049 r8:00000000 r7:0000003c r6:00000009 r5:00000000
[ 220.359660] r4:d8a31d7c r3:c15097ad
[ 220.363274] [<c0128aec>] (__warn.part.3) from [<c0128c40>] (warn_slowpath_fmt+0x64/0x88)
[ 220.371394] r7:c031643c r6:0000003c r5:c0e7e010 r4:c1108908
[ 220.377092] [<c0128be0>] (warn_slowpath_fmt) from [<c031643c>] (internal_create_group+0x324/0x398)
[ 220.386076] r3:bf009090 r2:c0e7e054
[ 220.389681] r7:bf00a048 r6:d8ba7a4c r5:d8c058c0 r4:d8ab2504
[ 220.395375] [<c0316118>] (internal_create_group) from [<c03164c8>] (sysfs_create_group+0x18/0x1c)
[ 220.404282] r10:c1108908 r9:00000000 r8:bf00a048 r7:00000006 r6:bf00a048 r5:00000006
[ 220.412135] r4:bf009208
[ 220.414705] [<c03164b0>] (sysfs_create_group) from [<c014ef44>] (module_param_sysfs_setup+0x7c/0xb8)
[ 220.423873] [<c014eec8>] (module_param_sysfs_setup) from [<c01d3cf8>] (load_module+0x1ba4/0x2594)
[ 220.432779] r9:d8a31f30 r8:00000006 r7:bf00a000 r6:c11dd480 r5:00000000 r4:bf00a048
[ 220.440556] [<c01d2154>] (load_module) from [<c01d494c>] (sys_finit_module+0xc4/0xe4)
[ 220.448421] r10:0000017b r9:00000000 r8:7fffffff r7:00000003 r6:022b6150 r5:00000000
[ 220.456273] r4:c1108908
[ 220.458842] [<c01d4888>] (sys_finit_module) from [<c0101000>] (ret_fast_syscall+0x0/0x28)
[ 220.467044] Exception stack(0xd8a31fa8 to 0xd8a31ff0)
[ 220.472129] 1fa0: 41ff0200 bea69ef5 00000003 022b6150 00000000 bea69ef5
[ 220.480340] 1fc0: 41ff0200 bea69ef5 bea69de4 0000017b 00000003 00000000 004e79b8 00000000
[ 220.488545] 1fe0: bea69c40 bea69c30 0042ecac b6eba1b0
[ 220.493630] r9:d8a30000 r8:c01011e4 r7:0000017b r6:bea69de4 r5:bea69ef5 r4:41ff0200
[ 220.501518] irq event stamp: 0
[ 220.504623] hardirqs last enabled at (0): [<00000000>] (null)
[ 220.510675] hardirqs last disabled at (0): [<c0125c54>] copy_process.part.3+0x2e4/0x1a84
[ 220.518868] softirqs last enabled at (0): [<c0125c54>] copy_process.part.3+0x2e4/0x1a84
[ 220.527046] softirqs last disabled at (0): [<00000000>] (null)
[ 220.533141] ---[ end trace d31065e9ec5213ff ]---
[ 220.548768] *** [module_param_demo_init:26]Build Time: Nov 24 2024 21:45:23, git version:15c3f15 ***
[ 220.558118] module_param_demo module init!
[ 220.562327] number=10
[ 220.564622] number_x=11
[ 220.567085] number_0=12
[ 220.569549] name=sumu
[ 220.571931] para[0] : 0
[ 220.574486] para[1] : 1
[ 220.577037] para[2] : 2
[ 220.579588] para[3] : 3
[ 220.582192] para[4] : 4
[ 220.584747] para[5] : 5
[ 220.587298] para[6] : 6
[ 220.589849] para[7] : 7
[ 220.592442] str1=demo有和前面一样的报错信息,但是最下面每个参数的值都发生了变化,和我们前面传递的参数都是对应的:
# insmod module_param_demo.ko number = 10 number_x = 11 number_0 = 12 name = "sumu" para = 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 str = "demo"2.3 /sys/module/模块名/parameters
不管我们有没有传递参数进去,我这里是以传递参数的加载方式为例,我们看一下 /sys/module/模块名:
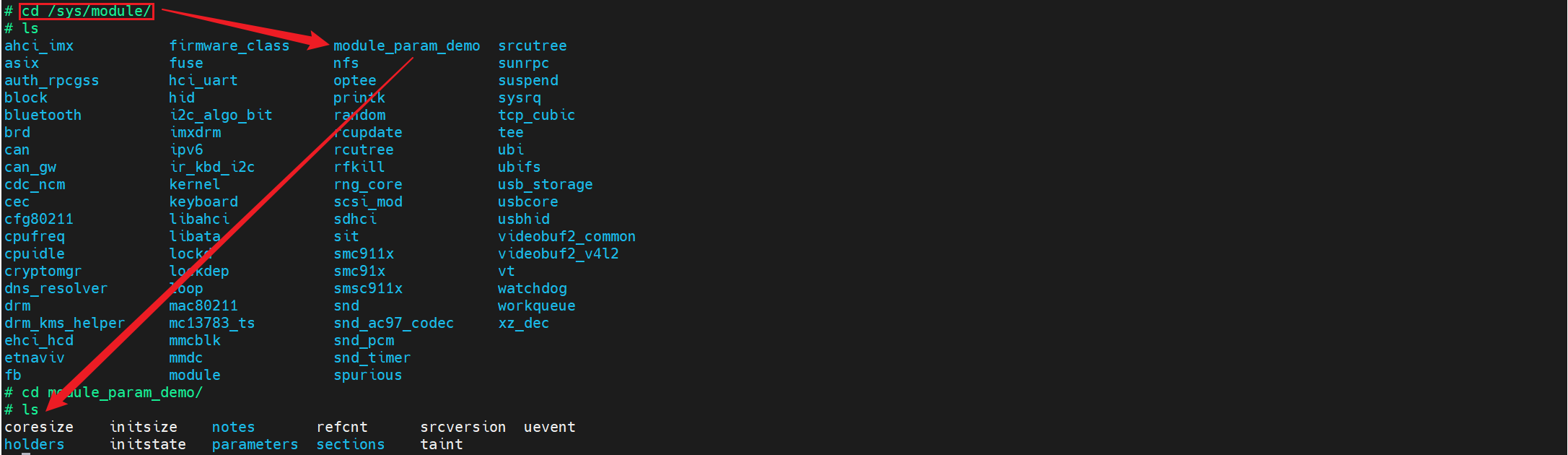
会发现这个目录下还有很多目录,包括我们要看的 parameters 目录,我们看一下这个目录下都有什么:
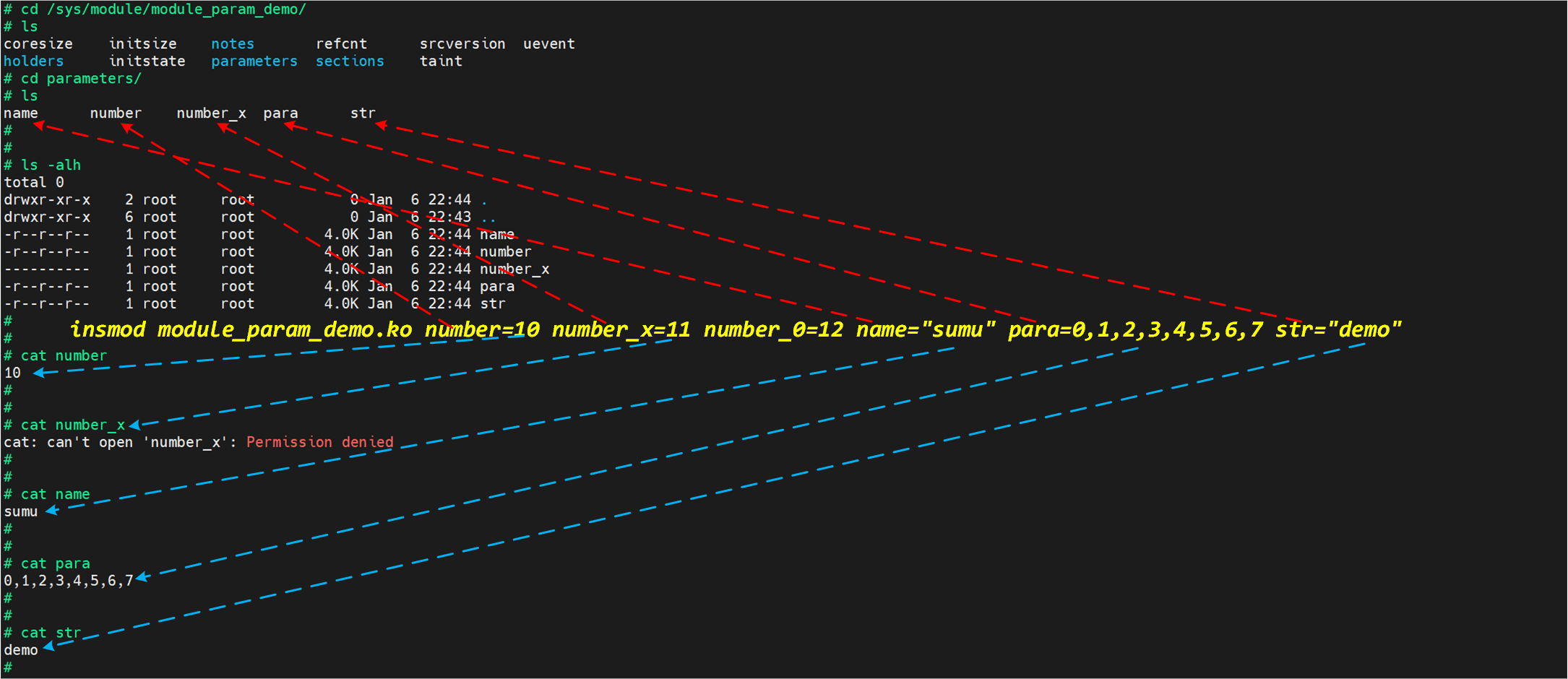
会发现,这不就是我们前面定义的几个内核模块参数嘛。不过这里会发现少了一个,少了 number_0 这个参数,因为我们前面给的权限是 0,所以这里没有权限查看这个参数,这里也就不会显示。