LV110-uboot-bin生成过程
一、目标文件
配置好 uboot 以后就可以直接 make 编译了,因为没有指明目标,所以会使用默认目标,主 Makefile 中的默认目标如下:
# That's our default target when none is given on the command line
PHONY := _all
_all:目标_all 又依赖于 all,在 Makefile 中如下所示 :
# If building an external module we do not care about the all: rule
# but instead _all depend on modules
PHONY += all
ifeq ($(KBUILD_EXTMOD),)
_all: all
else
_all: modules
endif如果 KBUILD_EXTMOD 为空的话 _all 依赖于 all 。这里不是单独编译模块,所以 KBUILD_EXTMOD 为空, _all 的依赖就是 all。
二、all 目标规则
在主 Makefile 中 all 目标规则如下:
all: $(ALL-y)
ifeq ($(CONFIG_DM_I2C_COMPAT)$(CONFIG_SANDBOX),y)
@echo >&2 "===================== WARNING ======================"
@echo >&2 "This board uses CONFIG_DM_I2C_COMPAT. Please remove"
@echo >&2 "(possibly in a subsequent patch in your series)"
@echo >&2 "before sending patches to the mailing list."
@echo >&2 "===================================================="
endif
#......
endif
@# Check that this build does not use CONFIG options that we do not
@# know about unless they are in Kconfig. All the existing CONFIG
@# options are whitelisted, so new ones should not be added.
$(call cmd,cfgcheck,u-boot.cfg)all 里面其实是大量的打印信息,主要还是要看它的依赖$(ALL-y)。
三、ALL-y
在顶层 Makefile 中, ALL-y 如下 :
# Always append ALL so that arch config.mk's can add custom ones
ALL-y += u-boot.srec u-boot.bin u-boot.sym System.map binary_size_check
ALL-$(CONFIG_ONENAND_U_BOOT) += u-boot-onenand.bin
#......
ALL-$(CONFIG_OF_HOSTFILE) += u-boot.dtb
ifneq ($(CONFIG_SPL_TARGET),)
ALL-$(CONFIG_SPL) += $(CONFIG_SPL_TARGET:"%"=%)
endif
#......
# Add optional build target if defined in board/cpu/soc headers
ifneq ($(CONFIG_BUILD_TARGET),)
ALL-y += $(CONFIG_BUILD_TARGET:"%"=%)
endif
#......
ifeq ($(CONFIG_MPC85xx)$(CONFIG_OF_SEPARATE),yy)
ALL-y += u-boot-with-dtb.bin
endif可以看出, ALL-y 一定包含 u-boot.srec、 u-boot.bin、 u-boot.sym、System.map、 u-boot.cfg 和 binary_size_check 这几个文件。根据 uboot 的配置情况也可能包含其他的文件,比如:
ALL-$(CONFIG_ONENAND_U_BOOT) += u-boot-onenand.binCONFIG_ONENAND_U_BOOT 就是 uboot 中跟 ONENAND 配置有关的,如果我们使能了 ONENAND,那么在.config 配置文件中就会有“CONFIG_ONENAND_U_BOOT = y”这一句。相当于 CONFIG_ONENAND_U_BOOT 是个变量,这个变量的值为“y”,所以展开以后就是:
ALL-y += u-boot-onenand.bin这个就是.config 里面的配置参数的含义,这些参数其实都是变量,后面跟着变量值,会在顶层 Makefile 或者其他 Makefile 中调用这些变量。
四、u-boot.bin
ALL-y 里面有个 u-boot.bin,这个就是我们最终需要的 uboot 二进制可执行文件,所作的所有工作就是为了它。在顶层 Makefile 中找到 u-boot.bin 目标对应的规则,如下所示:
ifeq ($(CONFIG_MULTI_DTB_FIT),y)
fit-dtb.blob: dts/dt.dtb FORCE
$(call if_changed,mkimage)
MKIMAGEFLAGS_fit-dtb.blob = -f auto -A $(ARCH) -T firmware -C none -O u-boot \
-a 0 -e 0 -E \
$(patsubst %,-b arch/$(ARCH)/dts/%.dtb,$(subst ",,$(CONFIG_OF_LIST))) -d /dev/null
u-boot-fit-dtb.bin: u-boot-nodtb.bin fit-dtb.blob
$(call if_changed,cat)
u-boot.bin: u-boot-fit-dtb.bin FORCE
$(call if_changed,copy)
else ifeq ($(CONFIG_OF_SEPARATE),y)
u-boot-dtb.bin: u-boot-nodtb.bin dts/dt.dtb FORCE
$(call if_changed,cat)
u-boot.bin: u-boot-dtb.bin FORCE
$(call if_changed,copy)
else
u-boot.bin: u-boot-nodtb.bin FORCE
$(call if_changed,copy)
endif可以搜索一下这个 CONFIG_MULTI_DTB_FIT,会发现是没有这个配置项的:
sumu@sumu-virtual-machine:~/7Linux/imx6ull-uboot$ grep -nRw "CONFIG_MULTI_DTB_FIT" ./
#......
./.config:654:# CONFIG_MULTI_DTB_FIT is not set所以走的是 else 这部分,我们再搜一下 CONFIG_OF_SEPARATE:
sumu@sumu-virtual-machine:~/7Linux/imx6ull-uboot$ grep -nRw "CONFIG_OF_SEPARATE" ./
# ......
./.config:649:CONFIG_OF_SEPARATE=y判断 CONFIG_OF_SEPARATE 是否等于 y,如果相等,那条件就成立。所以在这里是成立的。所以这一大段最后就是:
u-boot-dtb.bin: u-boot-nodtb.bin dts/dt.dtb FORCE
$(call if_changed,cat)
u-boot.bin: u-boot-dtb.bin FORCE
$(call if_changed,copy)这部分就是制作 u-boot-dtb.bin 和 u-boot.bin 的规则,目标 u-boot.bin 依赖于 u-boot-dtb.bin,命令为$(call if_changed, copy) , 这里调用了 if_changed ,if_changed 是一个函数 ,这个函数在 scripts/Kbuild.include 中有定义。而顶层 Makefile 中会包含 scripts/Kbuild.include 文件,这个前面已经说过了。 if_changed 在 scripts/Kbuild.include 中的定义如下:
if_changed = $(if $(strip $(any-prereq) $(arg-check)), \
@set -e; \
$(echo-cmd) $(cmd_$(1)); \
printf '%s\n' 'cmd_$@ := $(make-cmd)' > $(dot-target).cmd)这里有一些关于 if_changed 的描述在 scripts/Kbuild.include:
###
# if_changed - execute command if any prerequisite is newer than
# target, or command line has changed
# if_changed_dep - as if_changed, but uses fixdep to reveal dependencies
# including used config symbols
# if_changed_rule - as if_changed but execute rule instead
# See Documentation/kbuild/makefiles.txt for more info根据描述,在一些先决条件比目标新的时候,或者命令行有改变的时候, if_changed 就会执行一些命令。继续往后看就可以找到刚才的定义:
if_changed = $(if $(strip $(any-prereq) $(arg-check)), \
@set -e; \
$(echo-cmd) $(cmd_$(1)); \
printf '%s\n' 'cmd_$@ := $(make-cmd)' > $(dot-target).cmd)这里是函数 if_changed, if_changed 函数引用的变量比较多,也比较绕,我们只需要知道它可以从 u-boot-dtb.bin 生成 u-boot.bin 就行了。
五、u-boot-dtb.bin
1. 依赖目标
既然 u-boot.bin 依赖于 u-boot-dtb.bin,那么肯定要先生成 u-boot-dtb.bin 文件,顶层 Makefile 中相关代码如下:
u-boot-dtb.bin: u-boot-nodtb.bin dts/dt.dtb FORCE
$(call if_changed,cat)目标 u-boot-dtb.bin 又依赖于 u-boot-nodtb.bin, u-boot-nodtb.bin 的规则在 Makefile 中如下所示:
u-boot-nodtb.bin: u-boot FORCE
$(call if_changed,objcopy)
$(call DO_STATIC_RELA,$<,$@,$(CONFIG_SYS_TEXT_BASE))
$(BOARD_SIZE_CHECK)可以看到 u-boot-nodtb.bin 又依赖于 u-boot。
2. u-boot
2.1 u-boot 的依赖
u-boot 的规则在顶层 Makefile 中相关规则如下:
u-boot: $(u-boot-init) $(u-boot-main) u-boot.lds FORCE
+$(call if_changed,u-boot__)
ifeq ($(CONFIG_KALLSYMS),y)
$(call cmd,smap)
$(call cmd,u-boot__) common/system_map.o
endif
ifeq ($(CONFIG_RISCV),y)
@tools/prelink-riscv $@ 0
endif可以看到目标 u-boot 依赖于 u-boot-init、 u-boot-main 和 u-boot.lds, u-boot-init 和 u-boot-main 是两个变量,在顶层 Makefile 中有定义,值如下:
u-boot-init := $(head-y)
u-boot-main := $(libs-y)2.2 head-y
$(head-y)跟 CPU 架构有关,我们使用的是 ARM 芯片,所以 head-y 在 arch/arm/Makefile 中被指定为:
head-y := arch/arm/cpu/$(CPU)/start.o根据本篇笔记 “第一部分 第 11.3 变量导出” 小节,我们知道 CPU = armv7,因此 head-y 展开以后就是:
head-y := arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.o所以就有:
u-boot-init= arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.o2.3 libs-y
$(libs-y)在顶层 Makefile 中被定义为 uboot 所有子目录下 build-in.o 的集合,代码如下:
libs-y += lib/
libs-$(HAVE_VENDOR_COMMON_LIB) += board/$(VENDOR)/common/
libs-$(CONFIG_OF_EMBED) += dts/
libs-y += fs/
libs-y += net/
# ......
u-boot-dirs := $(patsubst %/,%,$(filter %/, $(libs-y))) tools examples
u-boot-alldirs := $(sort $(u-boot-dirs) $(patsubst %/,%,$(filter %/, $(libs-))))
libs-y := $(patsubst %/, %/built-in.o, $(libs-y))从上面的代码可以看出, libs-y 都是 uboot 各子目录的集合,最后:
libs-y := $(patsubst %/, %/built-in.o, $(libs-y))这里调用了函数 patsubst,将 libs-y 中的“/”替换为”/built-in.o”,比如“drivers/dma/”就变为了“drivers/dma/built-in.o”,相当于将 libs-y 改为所有子目录中 built-in.o 文件的集合。那么 uboot-main 就等于所有子目录中 built-in.o 的集合。
2.4 u-boot.lds 规则
上面的这个 u-boot 规则就相当于将以 u-boot.lds 为链接脚本,将 arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.o 和各个子目录下的 built-in.o 链接在一起生成 u-boot。u-boot.lds 的规则在 Makefile 中是这样的:
u-boot.lds: $(LDSCRIPT) prepare FORCE
$(call if_changed_dep,cpp_lds)2.5 built-in.o 怎么生成?
接下来的重点就是各子目录下的 built-in.o 是怎么生成的,以 drivers/gpio/built-in.o 为例,在 drivers/gpio/目录下会有个名为.built-in.o.cmd 的文件:
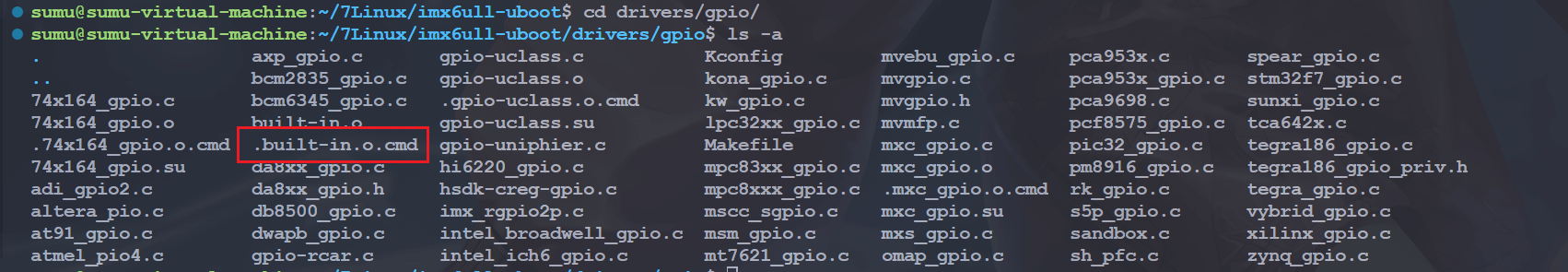
此文件内容如下:
cmd_drivers/gpio/built-in.o := arm-linux-gnueabihf-ld.bfd -r -o drivers/gpio/built-in.o drivers/gpio/gpio-uclass.o drivers/gpio/74x164_gpio.o drivers/gpio/mxc_gpio.o从命令“cmd_drivers/gpio/built-in.o”可以看出, drivers/gpio/built-in.o 这个文件是使用 ld 命令由文件 drivers/gpio/mxc_gpio.o 还有另外两个.o 生成而来的,其中 mxc_gpio.o 是 mxc_gpio.c 编译生成的.o 文件,其他两个也类似,这个是 NXP 的 I.MX 系列的 GPIO 驱动文件。这里用到了 ld 的“-r”参数,参数含义如下:-r –relocateable: 产生可重定向的输出,比如,产生一个输出文件它可再次作为‘ld’ 的输入,这经常被叫做“部分链接”,当我们需要将几个小的.o 文件链接成为一个.o 文件的时候,需要使用此选项。
2.6 u-boot 的生成
最终将各个子目录中的 built-in.o 文件链接在一起就形成了 u-boot,使用如下命令编译 uboot 就可以看到链接的过程:
make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- distclean
make V=1 ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- mx6ull_14x14_evk_defconfig
make V=1 ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- -j16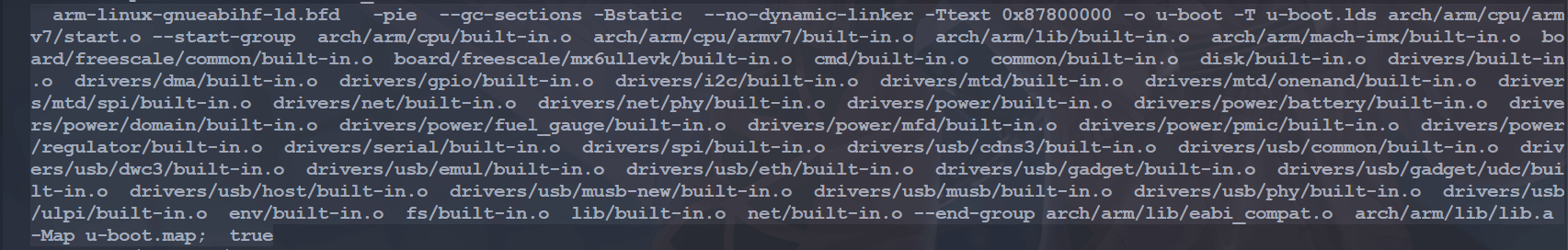
将其整理一下,内容如下:
arm-linux-gnueabihf-ld.bfd -pie --gc-sections -Bstatic --no-dynamic-linker -Ttext 0x87800000 \
-o u-boot -T u-boot.lds \
arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.o --start-group \
arch/arm/cpu/built-in.o \
arch/arm/cpu/armv7/built-in.o \
#......
lib/built-in.o \
net/built-in.o --end-group \
arch/arm/lib/eabi_compat.o \
arch/arm/lib/lib.a \
-Map u-boot.map; \
true可以看出最终是用 arm-linux-gnueabihf-ld.bfd 命令将 arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.o 和其他众多的 built_in.o 链接在一起,形成 u-boot。目标 all 除了 u-boot.bin 以外还有其他的依赖,比如 u-boot.srec 、 u-boot.sym 、 System.map、u-boot.cfg 和 binary_size_check 等等,这些依赖的生成方法和 u-boot.bin 很类似,这里就不再详细说明了。
六、总结一下
这个图是按照 uboot 2016.03 画的,2019.04 有所不同,2019.04 使用设备树了,但是流程大概都是一样的。
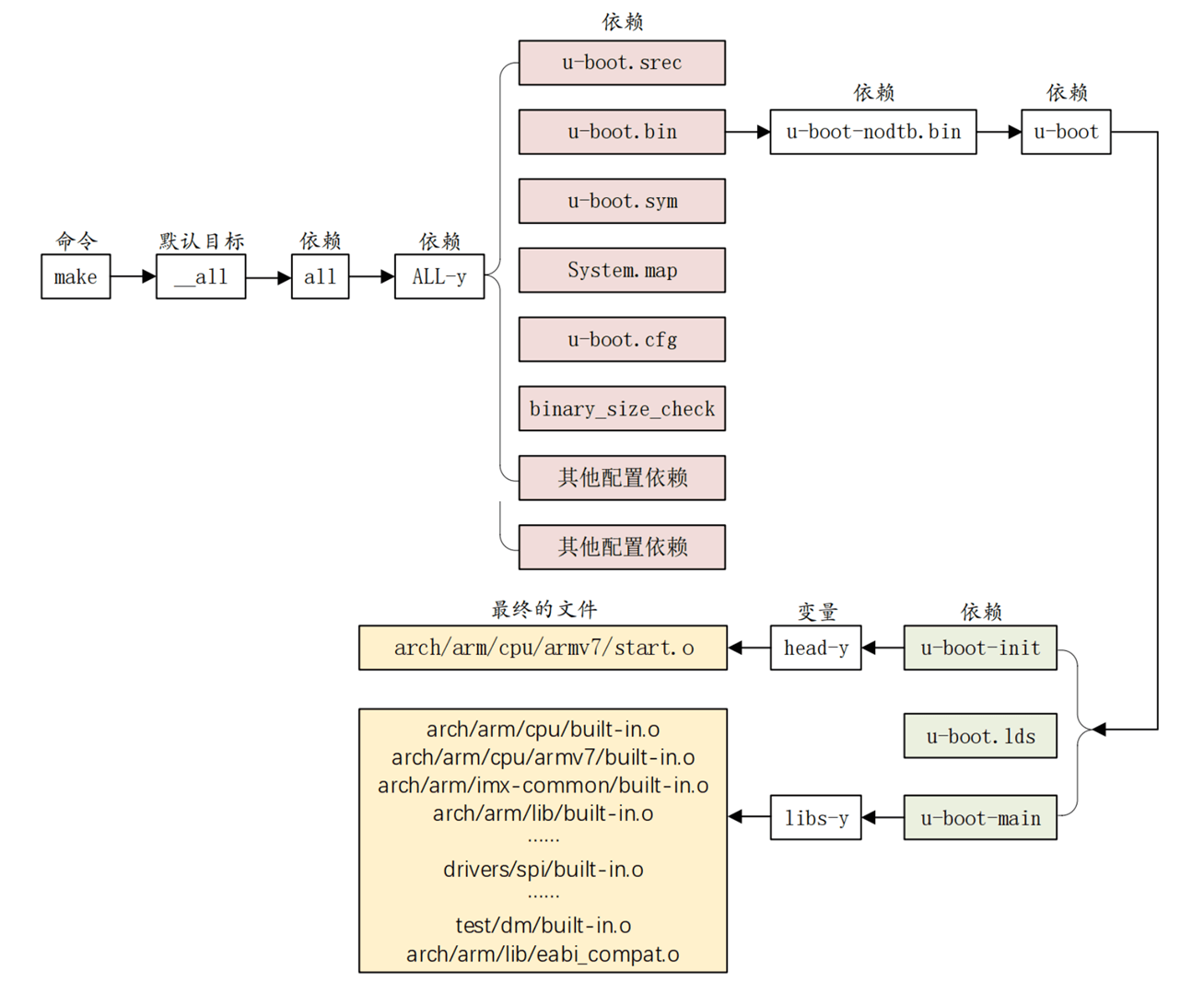
make xxx_defconfig: 用于配置 uboot,这个命令最主要的目的就是生成.config 文件。 make:用于编译 uboot,这个命令的主要工作就是生成二进制的 u-boot.bin 文件和其他的一些与 uboot 有关的文件,比如 u-boot.imx 等等。